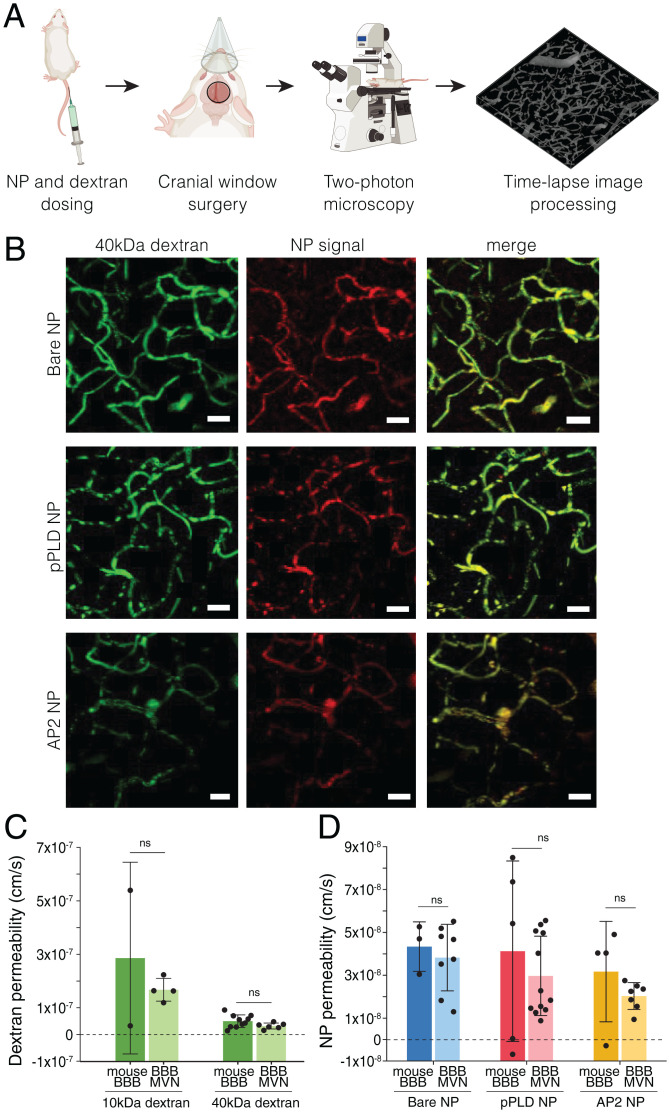
Fig. 3.
In vivo BBB permeability assessed by intravital microscopy is consistent with the in vitro BBB model. (A) Workflow of intravital imaging, in which fluorescent NPs and dextran are dosed systemically, and time-lapse imaging is performed in intact brain capillaries. (B) Representative images of 40-kDa dextran and NP formulations perfused in mouse BBB capillaries. (Scale bars, 20 µm.) (C) BBB permeabilities to fluorescently labeled dextran (10 and 40 kDa) in mouse BBB capillaries and in vitro BBB microvessels (no tumors). Points represents n = 1 device; n = 2 mice were considered for 10-kDa dextran and n = 10 mice for 40-kDa dextran. (D) BBB permeabilities to the three NP formulations in mouse BBB capillaries and in vitro BBB microvessels (no tumors). Points represent n = 1 ROI; n = 6 independent devices per condition were considered; n = 3 to 5 mice were considered per condition. Bars represent mean ± SD. ns, not significant. Statistical analyses are described in Materials and Methods.