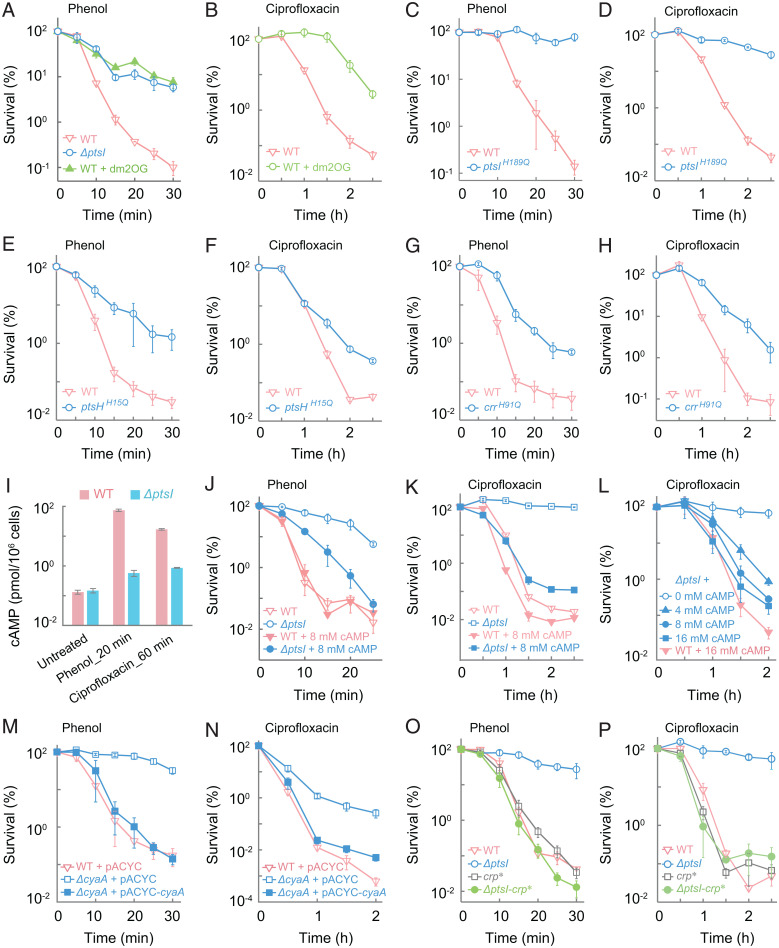
Fig. 3.
PtsI participates in phenol- and ciprofloxacin-mediated killing via early steps of the PTS phosphorelay and a subsequent interaction with the cAMP-Crp transcription regulatory axis. (A and B) Protective effect of dimethyl-2-oxoglutarate (dm2OG) on phenol- or ciprofloxacin-mediated killing. Wild-type E. coli (WT) was pretreated with 1 mg/mL dm2OG for 40 min before treatment with 3.5 mg/mL phenol (A) or 5× MIC ciprofloxacin (B) for the indicated times. As a reference, in A the ΔptsI mutant received no dm2OG pretreatment. (C–H) Protection due to abolished phosphorylation site in PtsI, PtsH, or Crr. Wild-type, a ptsI (H189Q) mutant (C and D), a ptsH (H15Q) mutant (E and F), and a crr (H91Q) mutant (G and H) were treated with 3.5 mg/mL phenol (C, E and G) or 5× MIC ciprofloxacin (D, F, and H) for the indicated times. (I) Suppression of stress-induced intracellular cAMP production by ΔptsI. Exponentially growing wild-type and ΔptsI mutant cells were treated with 3.5 mg/mL phenol or 5× MIC ciprofloxacin for the indicated times after which intracellular cAMP levels were determined. (J–L) Suppression of ptsI-mediated protection by exogenous cAMP. Wild-type and ΔptsI cells were pretreated with 8 mM cAMP for 15 min before addition of phenol (J) at 3.5 mg/mL or ciprofloxacin (K) at 5× MIC. L shows the concentration dependence of cAMP-mediated suppression of killing by 5× MIC ciprofloxacin with the ΔptsI mutant. (M and N) Deficiency of cyaA protects from phenol- and ciprofloxacin-mediated killing. Cultures of wild-type and ΔcyaA mutant cells were treated with 3.5 mg/mL phenol (M) or 10× MIC ciprofloxacin (N) for the indicated times. Complementation was observed with a plasmid-borne wild-type cyaA. (O and P) Suppression of the protective effect of ΔptsI by crp*. Exponentially growing cultures of wild-type, ΔptsI, crp*, and ΔptsI-crp* double-mutant cells were treated with 3.5 mg/mL phenol (O) or 5× MIC ciprofloxacin (P) for the indicted times. Data indicate average of three biological replicates; error bars indicate SEM. See SI Appendix, Fig. S4 and Tables S1 and S3 for supporting information.