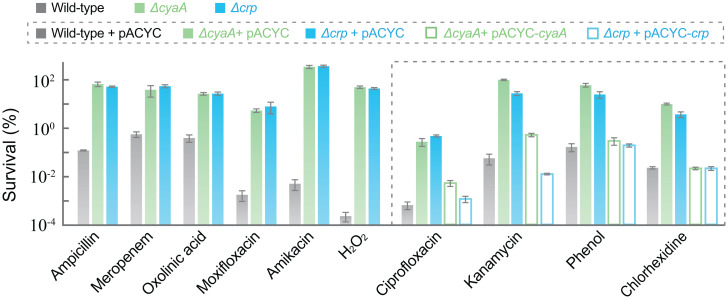
Fig. 4.
Deficiency of cyaA or crp protects from killing by diverse lethal stressors. Exponentially growing wild-type, ΔcyaA, and Δcrp cultures were treated with ampicillin (4× MIC for 3 h), meropenem (6× MIC for 8 h), oxolinic acid (10 MIC for 2 h), moxifloxacin (10× MIC for 2 h), amikacin (3× MIC for 2 h), hydrogen peroxide (25 mM for 30 min), ciprofloxacin (10× MIC for 2 h), kanamycin (5× MIC for 2 h), phenol (3.5 mg/mL for 25 min), or chlorhexidine (12 μg/mL for 4 h) prior to measurement of survival. Complementation with plasmid-borne wild-type cyaA or crp (pACYC-184-cyaA or pACYC-184-crp) was performed for four diverse stressors (ciprofloxacin, kanamycin, phenol, and chlorhexidine). (Also see SI Appendix, Figs. S5 F and I and S6 C, F, H, and I for more complementation data.) Data are averages of three biological replicates; error bars indicate SEM. See SI Appendix, Figs. S5 and S6 and Tables S1 and S3 for supporting information.