Fig. 3. O2 inactivates pyruvate formate-lyase.
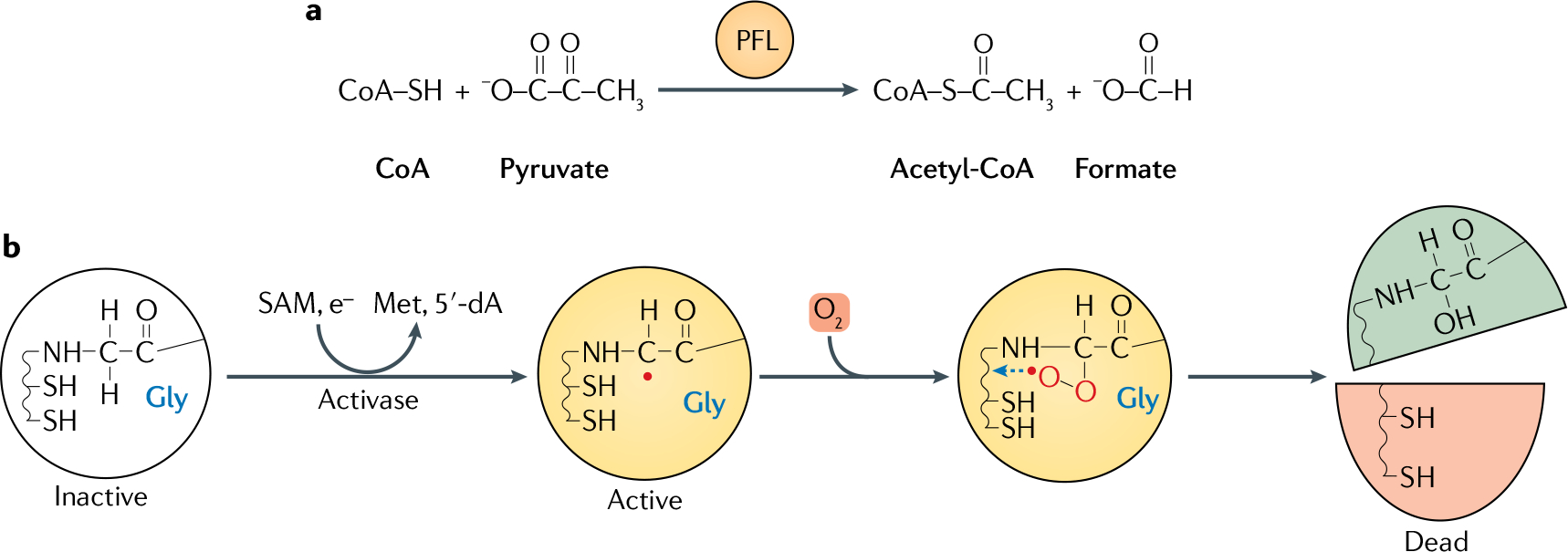
a | Pyruvate formate-lyase (PFL) catalyses pyruvate breakdown without producing NADH; this strategy is energetically economical because it avoids consuming acetyl-CoA to reoxidize NADH. Acetyl-CoA is then available for ATP synthesis (not shown). b | PFL is a prototype of the family of glycyl-radical enzymes. The glycyl radical is produced as a post-translational modification by PFL activating enzyme (activase), which activates PFL through a S-denosylmethionine (SAM)-dependent reaction, in which the monoelectronic reduction of SAM generates a 5-deoxyadenosyl radical (5′-dA) and methionine as by-products. Oxygen (O2) inactivates PFL by adducting the glycyl radical, forming a hydroperoxyl radical species that finally cleaves the polypeptide.
