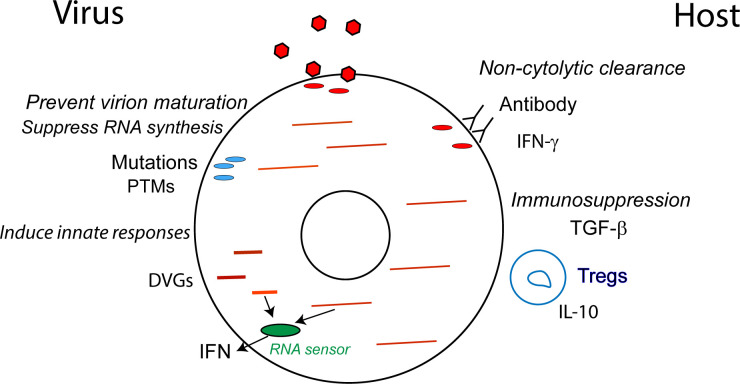
Fig 3. Mechanisms for suppressing production of infectious virions.
Several mechanisms exist whereby the virus and host can suppress the production of infectious virions to facilitate the survival of infected cells and viral RNA persistence. For example, the virus may acquire mutations that decrease virion assembly, induce innate responses, or decrease RNA synthesis, while the host employs antiviral immune responses that facilitate infected cell survival. DVG, defective viral genome; IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; PTM, posttranslational modification; TGF, transforming growth factor.