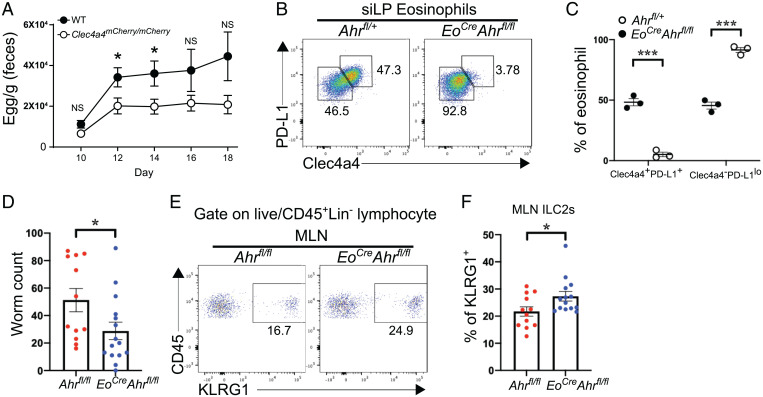
Fig. 4.
Clec4a4+ eosinophils modulate type 2 immunity during helminth infection. (A) Egg counts in feces of WT and Clec4a4-deficient (Clec4a4mCherry/mCherry) mice (n = 13 in each group) at the indicated time points during H. polygyrus infection. (B) Expression of Clec4a4 and PD-L1 in siLP eosinophils derived from Ahrfl/+ and EoCreAhrfl/fl mice. (C) Frequency of Clec4a4+PD-L1+ and Clec4a4−PD-L1lo siLP eosinophils in Ahrfl/+ and EoCreAhrfl/fl mice (n = 3 each group). (D) Worm counts in Ahrfl/fl (n = 12) and EoCreAhrfl/fl (n = 15) mice at day 6 postinfection with N. brasiliensis. (E) Representative percentages of KLRG1+ ILC2s among CD45+ cells in mesenteric lymph nodes (MLNs) of Ahrfl/fl and EoCreAhrfl/fl mice. A gate was applied on lineage-negative cells. Lineage markers included CD3, CD4, CD8, CD19, and NK1.1. (F) Frequency of ILC2s in MLNs from Ahrfl/fl (n = 12) and EoCreAhrfl/fl (n = 14) mice at day 6 postinfection with N. brasiliensis. Results are shown as mean ± SEM. P values were calculated using the two-tailed Student’s t test or one-way ANOVA and the Tukey's multiple comparisons test. NS, not significant. *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001.