FIGURE 2.
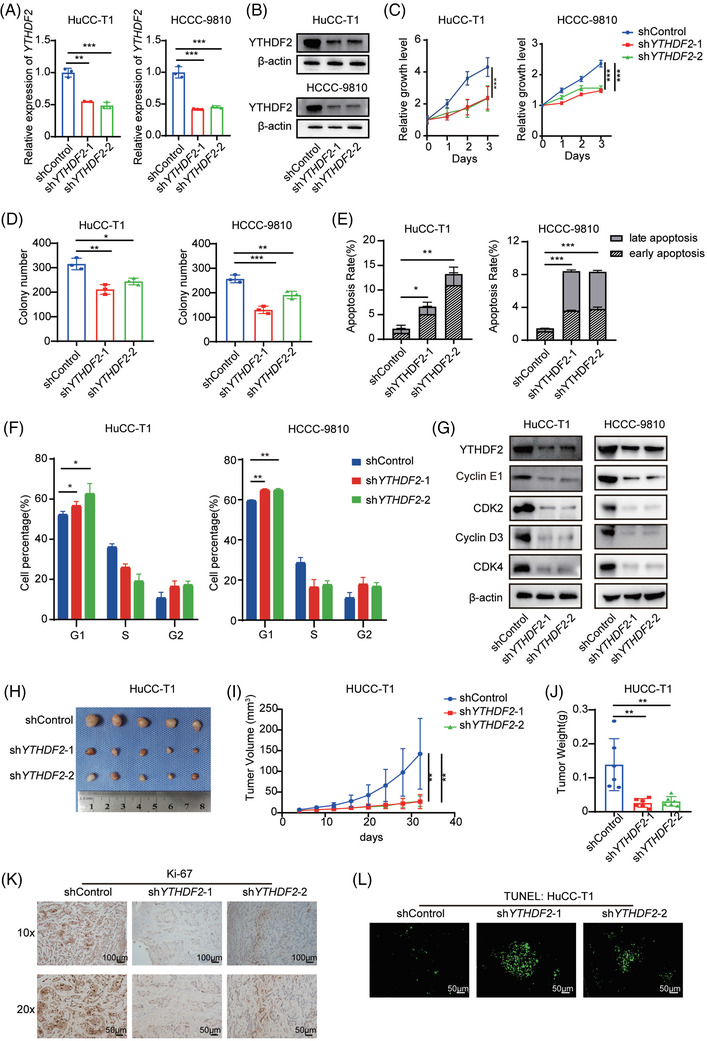
Knockdown of YTHDF2 significantly inhibits ICC cell proliferation, promotes apoptosis and arrests cell cycle in G0/G1 stage. (A) Relative mRNA expression of YTHDF2 in HuCC‐T1 and HCCC‐9810 cells transfected with shControl or shYTHDF2. (B) The protein expression of YTHDF2 in HuCC‐T1 and HCCC‐9810 cells transfected with shControl or shYTHDF2 were measured by western blotting. (C) Cell viability of HuCC‐T1 and HCCC‐9810 cells transfected with shControl or shYTHDF2. (D) Colony formation analysis of HuCC‐T1 and HCCC‐9810 cells transfected with shControl or shYTHDF2. (E) Apoptosis analysis of HuCC‐T1 and HCCC‐9810 cells transfected with shControl or shYTHDF2. (F) Cell cycle analysis of HuCC‐T1 and HCCC‐9810 cells transfected with shControl or shYTHDF2. (G) Immunoblotting to measure YTHDF2, CDK2, cyclinD3, cyclinE1 and CDK4 protein levels in HuCC‐T1 and HCCC‐9810 cells transfected with shControl or shYTHDF2. (H) The mice were executed 32 days post‐implantation of shControl or shYTHDF2‐transfected HuCC‐T1 cells and the tumours from respective groups were photographed. (I) Tumour growth curves post‐implantation of shControl or shYTHDF2‐ transfected HuCC‐T1 cells. Tumour volume was calculated every 4 days. (J) Tumour weight of each group was measured. (K) Representative IHC staining of Ki67 in tumours with different treatments. (L) Representative images of TUNEL analysis in tumours with different treatments. The data are presented as mean ± SD and compared by t‐test. *p < .05; **p < .01; *** p < .001
