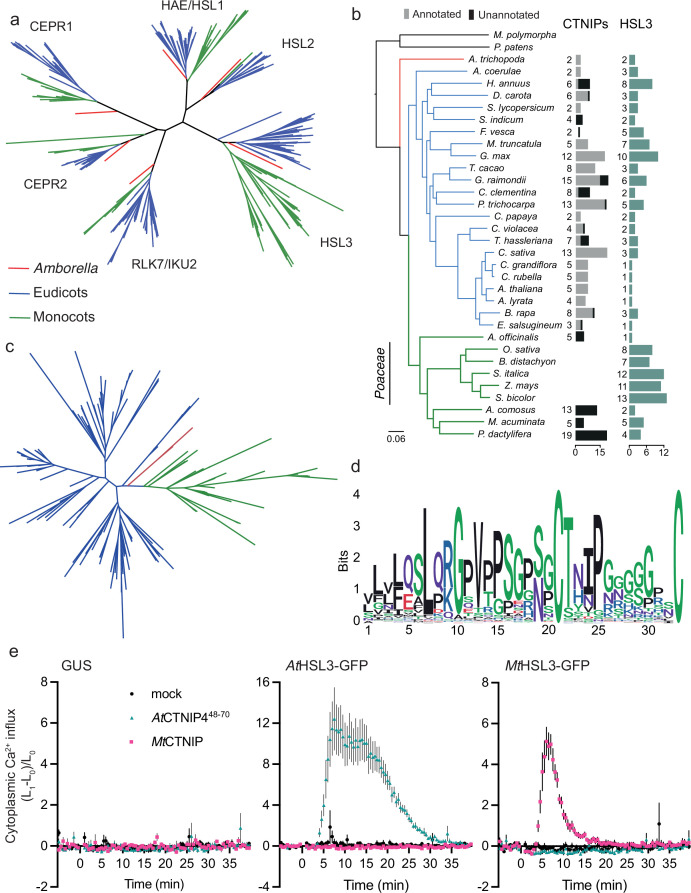
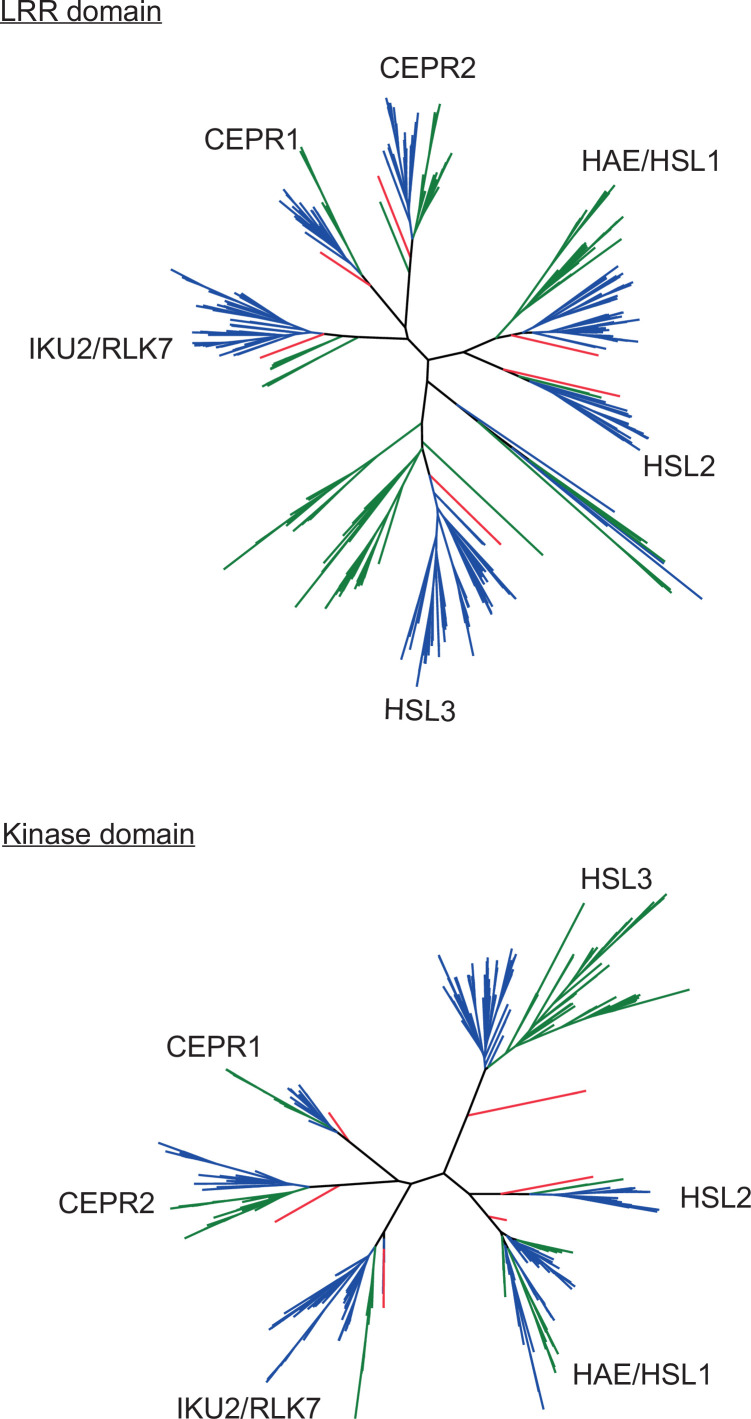
Figure 4. The HSL3-CTNIP signalling module predates extant angiosperms.
(a) Phylogeny of the full-length amino acid sequences of HAE/HSL/CEPR/RLK7/IKU2 clade of receptor kinases. Eudicot sequences are indicated in blue, monocot sequences in green, and Amborella sequences in red. Clades are named based upon the Arabidopsis genes. Alignment shown in Supplementary file 14. Further details of species, sequence identification, alignment, and phylogeny generation are described in the Materials and methods. (b) Species tree with number of CTNIP and HSL3 orthologs identified. Annotated CTNIPs are shown in grey whilst unannotated CTNIPs are shown in black. Sequences are shown in Supplementary files 10 and 16. (c) Phylogeny of the full-length amino acid sequences of CTNIPs. Eudicot sequences are indicated in blue, monocot sequences in green, and Amborella sequences in red. Sequences shown in Supplementary file 10. Further details of species, sequence identification, alignment, and phylogeny generation are described in the Materials and methods. (d) Sequence logo generated from CTNIP alignment from (c) using the R-package ggseqlogo. Amino acids are coloured based on their biochemical properties: red = acidic; blue = basic; black = hydrophobic; purple = neutral, and green = polar. (e) Cytoplasmic calcium influx measured after treatment with 1 μM CTNIP in p35S::AEQUORIN Nicotiana benthamiana leaf disks transiently expressing the defined construct, relative to pre-treatment (n = 8 leaf disks). Points represent mean; error bars represent SEM. Experiments were repeated and analysed three times with similar results. HSL3, HAESA-LIKE 3.