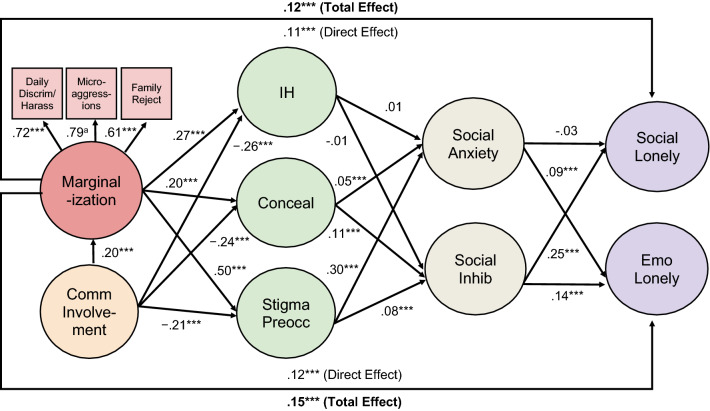
Fig. 3.
Structural equation model linking marginalization and loneliness, adjusted for dispositional negative affectivity. Notes: Daily Discrim/Harass = everyday discrimination/harassment, Family Reject = family rejection, Comm Involvement = community involvement, IH = internalized homonegativity, Conceal = concealment, Stigma Preocc = stigma preoccupation, Social Inhib = social inhibition, Social Lonely = social loneliness, Emo Lonely = emotional loneliness. For ease of presentation, direct associations between community involvement/proximal stress and both forms of loneliness are not shown, nor are direct associations between marginalization/community involvement and social anxiety/inhibition. The following correlated residuals (essentially factor correlations) are also not shown: internalized homonegativity and concealment (r = .36, p < .001), internalized homonegativity and stigma preoccupation (r = .49, p < .001), concealment and stigma preoccupation (r = .38, p < .001), social anxiety and social inhibition (r = .17, p < .001), and social and emotional loneliness (r = .72, p < .001). All values are standardized regression coefficients. a Strongest path fixed to 1.0 for statistical identification, thus p-value cannot be computed. ***p < .001, **p < .01