Fig. 1.
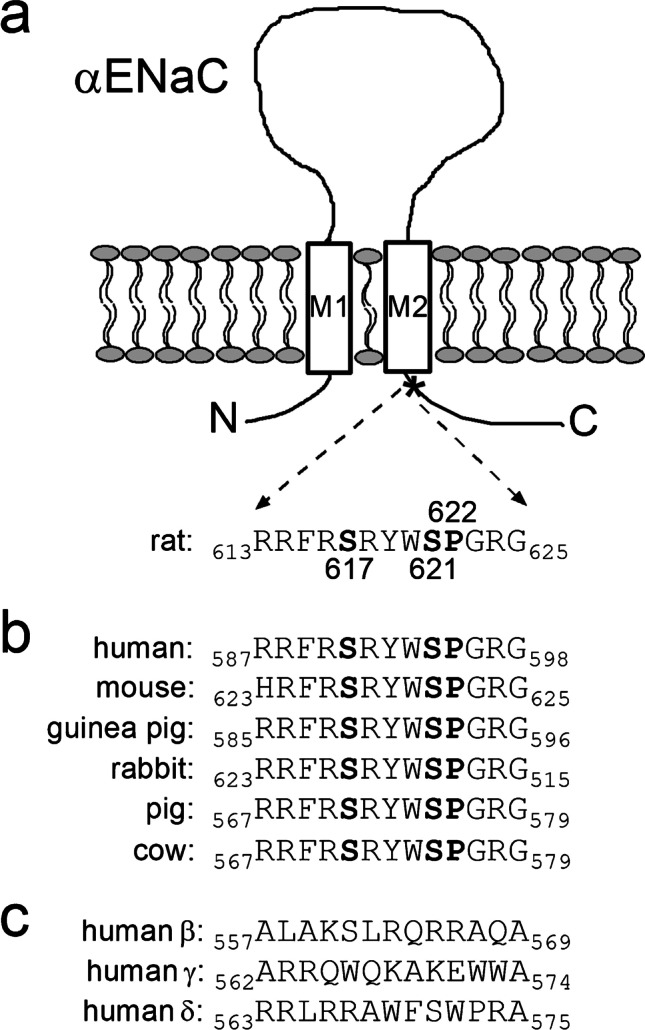
Two serine residues and one proline residue are highly conserved in a C-terminal region of αENaC close to the second transmembrane domain. a Schematic representation of αENaC illustrating the extracellular loop, two transmembrane domains (M1 and M2), and intracellular N- and C-termini. The amino acid sequence of rat αENaC (residues 613–625) corresponds to the C-terminal region indicated by a star (*) and contains the serine residues 617 (S617) and 621 (S621) and the proline residue 622 (P622) highlighted in bold. b Amino acid sequence alignment of this highly conserved C-terminal region from several mammalian αENaC subunits. The residues homologous to S617, S621, and P622 in rat αENaC are highlighted in bold. c Amino acid sequence alignment of homologous C-terminal regions from human β-, γ-, and δENaC subunits
