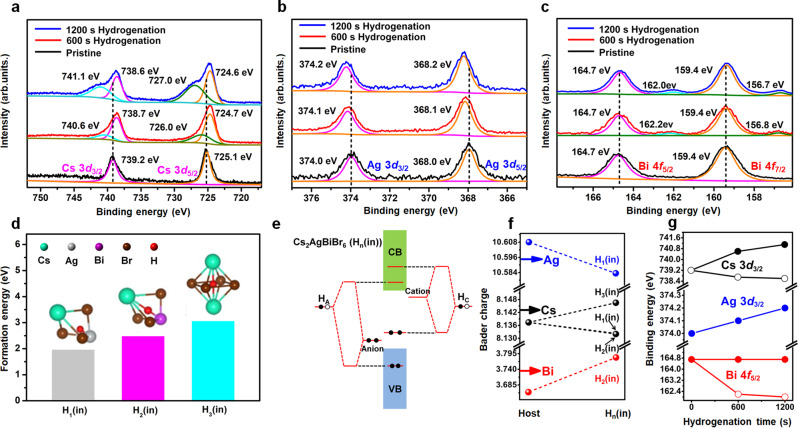
Fig. 5. Analyses on the chemical environment of Cs2AgBiBr6 during hydrogenation treatment.
a–c X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) spectra of Cs 3d, Ag 3d and Bi 4 f in Cs2AgBiBr6 films with different hydrogenation time (0 s, 600 s and 1200 s). d The formation energies of H1(in), H2(in) and H3(in). Here, Hn(in), where n = 1, 2, or 3, presents the H atom in the interstitial position of the Hn polyhedrons surrounded by Cs-Br-Ag (H1), Cs-Br-Bi (H2), and Cs-Br-Cs (H3), respectively. Cs, Ag, Bi, Br and H atoms are represented by cyan, light gray, purple, brown and red dots, respectively. e Schematic band coupling models of Hn(in) showing energy level positions when the H 1 s orbital is coupled to anion (forming donor) and cation (forming acceptor) levels (HA (coupled from interstitial Hn(in) and anion) and HC (coupled from interstitial Hn(in) and cation)). f Bader charge variations of Ag, Bi, and Cs atoms in the host and next to the interstitial H* in the Hn(in) polyhedrons. g The variation tendency of binding energy of Cs 3d3/2, Ag 3d3/2 and Bi 4f5/2 peaks as the increase of hydrogenation time.