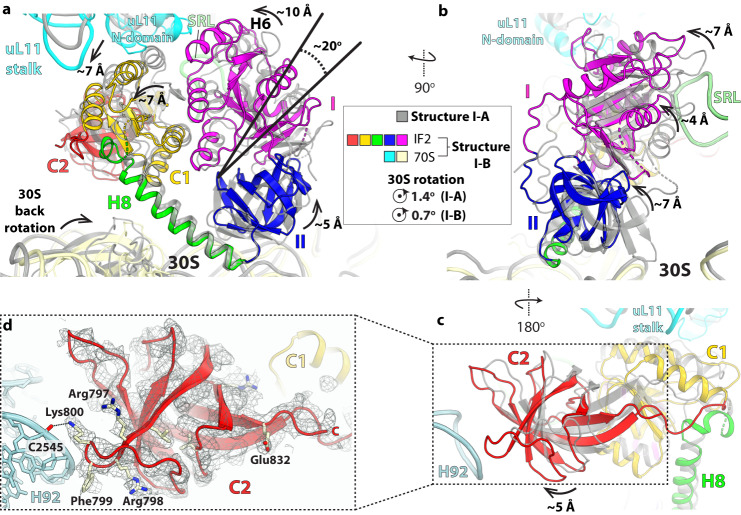
Fig. 6. Compact IF2 is loosely bound to the ribosome in structure I-B.
a Alignment of the 23 S rRNA in structures I-A and I-B shows that domain I (G-domain) rotates inward by ~20° around the SRL in structure I-B (colored domains) relative to structure I-A (gray). The center of rotation was taken around residue Gly589 in domain II. The maximum displacement at the outskirt of domain I is ~10 Å, ~7 Å for domain C1, and ~5 Å for domain II. Concomitantly, the uL11-stalk moves inward by ~7 Å together with domain C1. In structure I-B, helix H6 in the G-domain of compact IF2 is proximal to the N-domain of ribosomal protein uL11. The displacement of domain II away from the 30 S subunit in structure I-B, combined with the reverse rotation of the 30 S subunit between structure I-A (~1.4°) and I-B (~0.7°), weakens the binding of IF2-GDP to the ribosome in structure I-B. b Orthogonal view of panel a showing that in structure I-B the G-domain moves farther from the SRL by ~4 Å, which may facilitate IF2-GDP dissociation from the ribosome. c In structure I-B, the rotation of IF2-GDP around the SRL brings domain C2 (red) near 23 S rRNA helix H92. d EM density map of domain C2 in structure I-B shows that residues Phe799 and Lys800 form a complementary surface with H92. We note that in extended IF2 residue Phe799 interacts with the fMet residue attached to fMet-tRNAifMet in structures II-A and II-B (see Supplementary Fig. 8b).