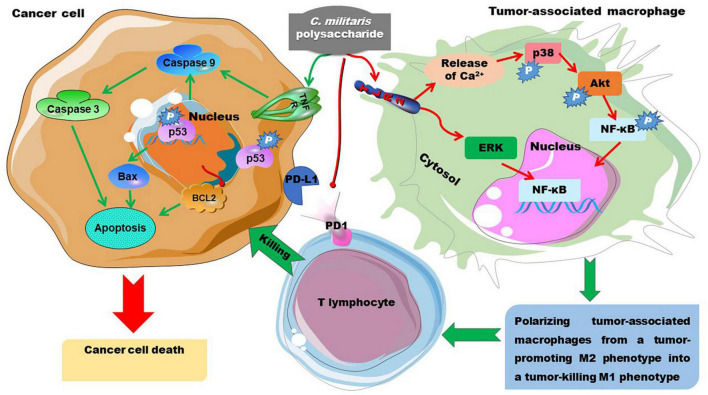
FIGURE 10.
The anti-tumor mechanisms of C. militaris-derived polysaccharides. C. militaris-derived polysaccharides induce cancer cell death by enhancing apoptosis-associated signaling. Alternatively, they polarize tumor-associated macrophages from M2 to M1 phenotype, thereby promoting the cancer cell killing activity of T lymphocytes. AKT/PKB, phosphoinositide-3-kinase/protein kinase B; Bax, B cell leukemia/lymphoma 2-associated X protein; Bcl-2, B cell leukemia/lymphoma 2; ERK, extracellular regulated kinase; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-B; PD-1, programmed death-1; PD-L1, programmed death lignd-1.