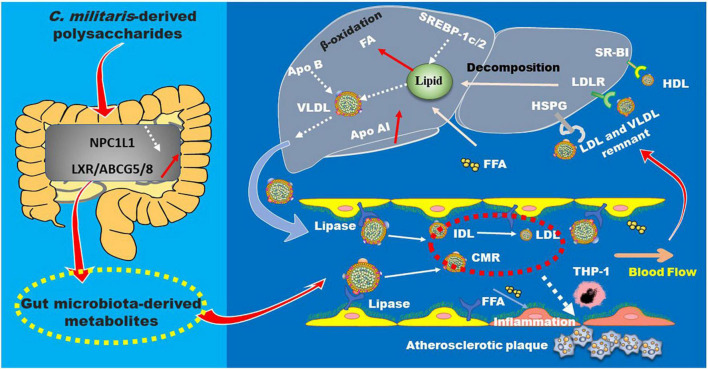
FIGURE 9.
The lipid-lowering mechanisms of C. militaris-derived polysaccharides. These polysaccharides are found to modulate multiple genes and proteins related to lipid absorption and metabolism in the plasma, small intestine, and liver, thereby improving hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis. ABC, ATP-binding cassette; Apo, apolipoprotein; CRM, chylomicron remnant; FFA, free fatty acid; HSPG, heparan sulfate proteoglycan; IDL, intermediate density lipoprotein; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; LDLR, low-density lipoprotein receptor; LRP1, LDLR-related protein 1; LXRα, liver X receptor α; NPC1L1, Niemann-Pick C1-like protein 1; SR-B1, scavenger receptor B type 1; SREBP, sterol regulatory element-binding protein; VLDL, very low-density lipoprotein.