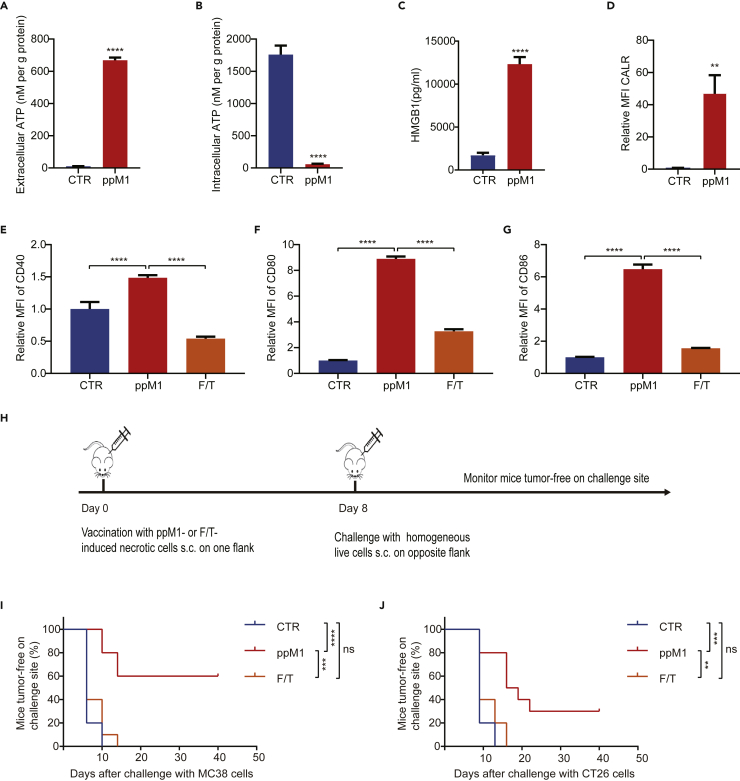
Figure 3.
ppM1 treatment induced ICD of tumor cells both in vitro and in vivo
(A–D) Extracellular ATP (A) and intracellular ATP (B) detection after ppM1 treatment for 2 h, extracellular HMGB1 (C) detection after ppM1 treatment for 8 h, exposure of calreticulin (D) on membrane after ppM1 treatment for 1 h.
(E–G) Flow cytometry measurements of BMDC maturation markers (CD40, CD80, and CD86) after coculturing with necroptotic MC38 cells induced respectively by ppM1 or freeze-thawing cycles.
(H) The schedule of prophylactic tumor vaccination experiments in Figures 3I and 3J.
(I and J) Rechallenges of tumor inoculation after immunization with 3×106 necroptotic cells induced by ppM1 or necrotic cells induced by F/T on both MC38-bearing C57BL/6 (I) (n = 10) and CT26-bearing BALB/c mice (J) (n = 10). Representative of 3 independent experiments in (A–G). All error bars represent SDs. (A–D) was analyzed with two-tailed unpaired t test, (E–G) was analyzed with 1-way ANOVA, (I–J) was analyzed with log rank (Mantel–Cox) test. ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. (See also Figure S7).