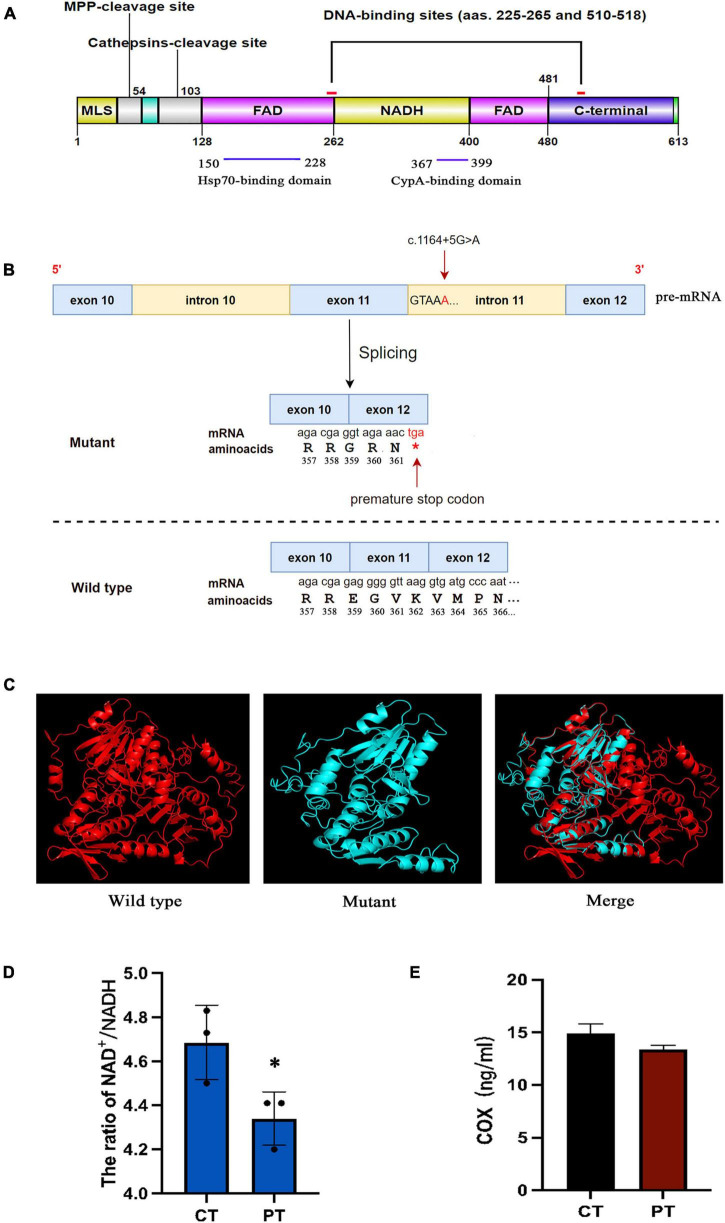
FIGURE 4.
(A) Schematic model representing the AIF protein. AIF is a flavoprotein (with an oxidoreductase enzymatic activity) containing a FAD-bipartite domain (amino-acids 128–262 and 401–480), a NADH-binding motif (amino-acids 263–400), and a C-terminal domain (amino-acids 481–608) where the proapoptotic activity of the protein resides. In addition, it has a Mitochondria Localization Sequence (MLS, amino-acids 1–41) placed in its N-terminal region. AIF also possesses two DNA-binding sites, which are located in amino-acids 255–265 and 510–518, respectively. (B) The mutant causes a frameshift resulted in the change of amino acid coding after R358, and the early termination codon was generated at the position of amino acid 362. (C) Protein structure modeling of wild-type and mutated AIFM1. A part of the amino acid sequence has been eliminated in the mutated protein compared to the wild type protein. (D) The NAD+/NADH ratios in fibroblasts of patient and control. (E) The human COX of cell culture supernatant in patient and control. *Statistically significant difference at p < 0.05.