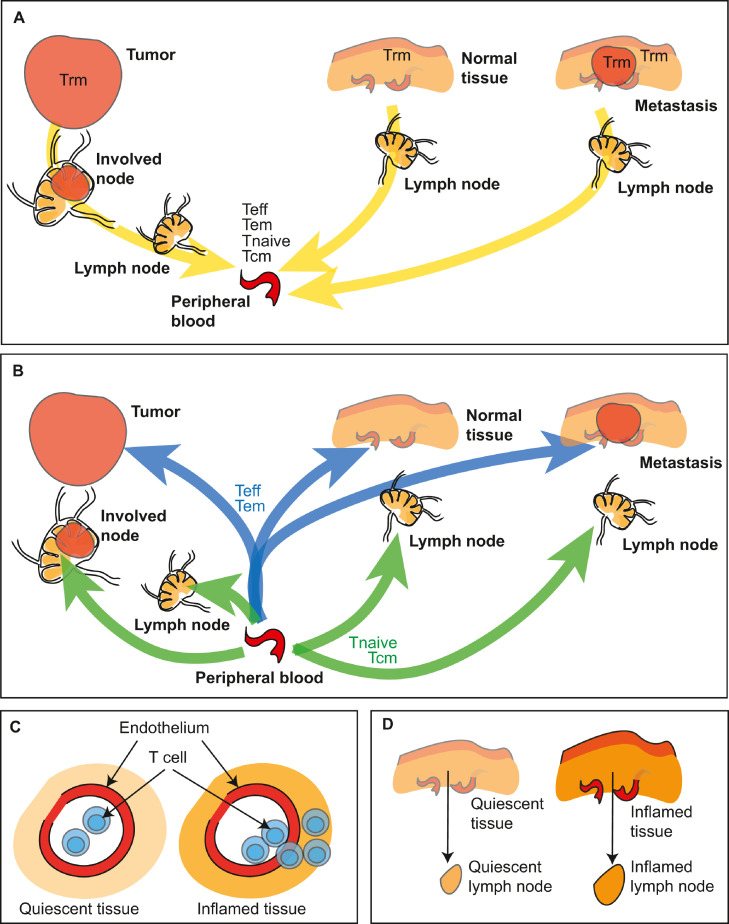
Fig. 5.
Trafficking of T cells is not antigen-directed.
A) T cells that exit the tumor pass through the lymphatic chain before re-entering the peripheral blood at the thoracic duct. Similar recirculation pathways return all T cell populations except tissue resident memory cells (Trm) to the peripheral circulation. B) Once in the peripheral blood, effector cells and effector memory cells (Teff, Tem) can be recruited back to the tumor, they may enter normal tissues or metastatic sites according to local inflammatory conditions. Naive T cells and central memory T cells (Tnaive, Tcm) can directly enter lymph nodes and recirculate without entering peripheral tissues. C) T cell entry to any particular tumor, tissue or lymph node is more likely if there is local inflammation that results in upregulation of adhesion molecules on the vasculature and chemokines. D) Inflammation in a tissue site can be propagated via the draining lymphatics to increase entry of T cells to the draining lymph node. Together, these features ensure additional surveillance of inflamed tissues and lymph nodes by recirculating T cells, but relative ignorance of tumors and metastases that are not inflamed.