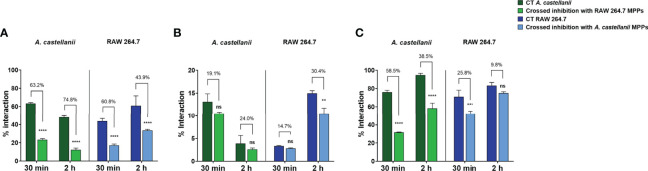
Figure 6.
Acanthamoeba castellanii and RAW mannose-binding lectins share the same binding targets on the fungal cell wall. (A) Candida albicans, (B) Cryptococcus neoformans and (C) Histoplasma capsulatum yeasts were pre-incubated with 50 µg/mL of either A. castellanii or RAW 264.7 MPPs. After this stage, cross-inhibitions were evaluated, where yeasts pre-treated with RAW 264.7 MPPs interacted with A. castellanii (light green bar) and compared to controls in the absence of inhibition (dark green bar). Additionally, yeasts pre-treated with A. castellanii MPPs interacted with RAW 264.7 macrophages (light blue bar), and compared to controls in the absence of inhibition (dark blue bar). Interactions were performed for 30 min and 2 h, to evaluate the initial fungal adhesion and the late interactions, respectively. Inhibition percentages (numbers above bars) were calculated from the interaction percentages as follows: (Control - Pre-treated group) x 100/Control. The statistical significances comparing inhibition x controls are represented above each group (**p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001; ns, not significant). The bars represent the average of three independent experiments, performed in triplicates.