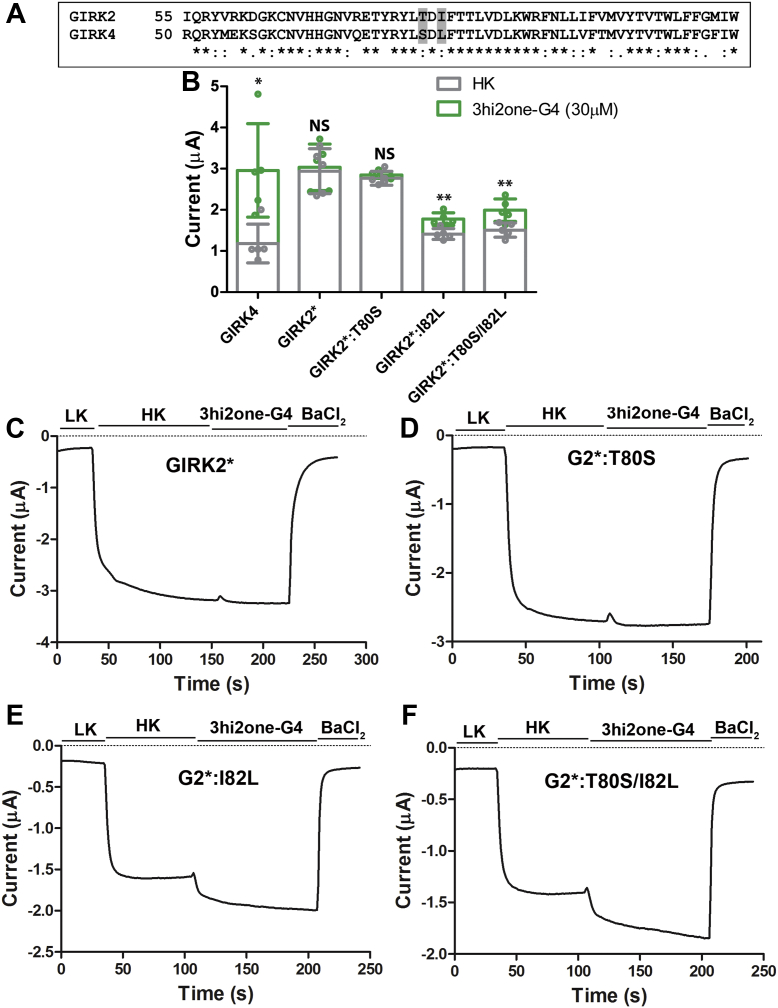
Figure 6.
3hi2one-G4 activates the GIRK2∗ channel mutants expressed in Xenopus oocytes.A, local sequence alignment between GIRK2 and GIRK4 near the slide helix region. Residues T80 and I82 in GIRK2; S75 and L77 in GIRK4 are highlighted in gray (∗: conserved, :: semiconserved, and .: similar residues). B, GIRK4, GIRK2∗, and mutant channels basal (HK, gray bars), and 3hi2one-G4 activator–induced current (green bars). The asterisks indicate significant differences between basal and 3hi2one-G4–induced currents by unpaired Student's t tests (∗∗p < 0.01, ∗p < 0.05) (data are mean ± SD, n = 5). C, representative traces of responses to the 3hi2one-G4 compound (30 μM) of GIRK2∗ channel. D, GIRK2∗:T80S. E, GIRK2∗:I82L. F, GIRK2∗:T80S/I82L. GIRK, G protein–sensitive inwardly rectifying potassium channel; HK, high potassium; 3hi2one, 3-[2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-oxoethyl]-3-hydroxy-1-(1-naphthylmethyl)-1,3-dihydro-2H-indol-2-one.