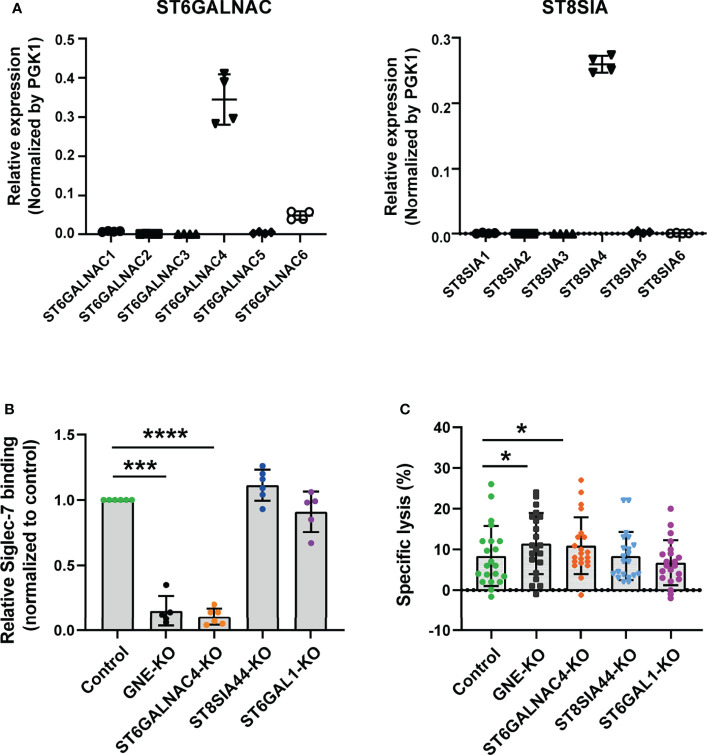
Figure 4.
ST6GalNAc-IV is responsible for Siglec-7 ligand glycotope synthesis. (A) Sialyltransferases expressed in JVM-3. The transcript level for ST6GALNAC4 was the highest among ST6GALNACs, whereas that for ST8SIA4 was the highest among ST8SIAs. Bars represent mean ± SD of technical quadruplicates. (B) Effect of sialyltransferase KO on Siglec-7–Fc binding. GNE and sialyltransferase genes (ST6GALNAC4, ST8SIA4, and ST6GAL1) in JVM-3 were disrupted with CRISPR–Cas9 technology, and the cells were subjected to staining with Siglec-7–Fc. The disruption of GNE and ST6GALNAC4 led to a marked reduction in Siglec-7–Fc binding, whereas the disruption of ST8SIA4 and ST6GAL1 did not. Data was normalized by the Siglec-7–Fc binding (in MFI) to control JVM-3 cells. ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test. Bars represent mean ± SD of 6 independent experiments. (C) Effect of sialyltransferase KO on NK cell cytotoxicity. Sialyltransferase KO and control JVM-3 cells were subjected to NK cell cytotoxicity assay. The disruption of GNE and ST6GALNAC4 led to increased sensitivity of JVM-3 cells to NK cytotoxicity, whereas the disruption of ST8SIA4 and ST6GAL1 did not (*P < 0.05, repeated-measures one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test). Bars represent mean ± SD of 21 independent experiments.