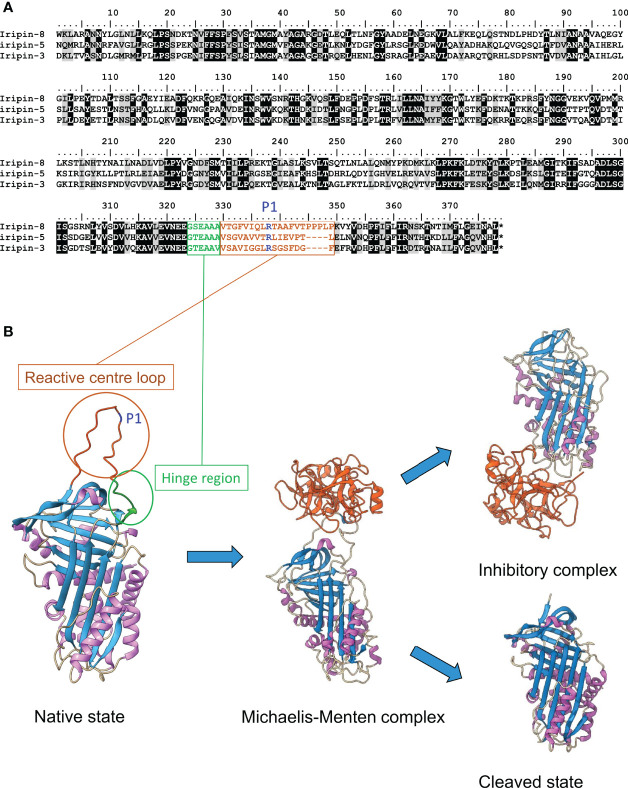
Figure 1.
Structure of serpins and their mechanism of inhibition. (A) Sequence alignment of three characterized serpins from I. ricinus. RCL is highlighted in brown, P1 site in blue and hinge region in green. (B) Tertiary structures of four most common serpin conformation states. Native state is presented with highlighted RCL, P1 site and hinge region highlighted with the same colors as in the alignment. It forms non-covalent Michaelis-Menten complex with target protease, which can further end up as a covalent inhibitory complex or as cleaved inactive state. Used structures were downloaded from RCSB Protein Data Bank and prepared in ChimeraX (Pettersen et al., 2021). Asterisk in the alignment represents the stop codon.