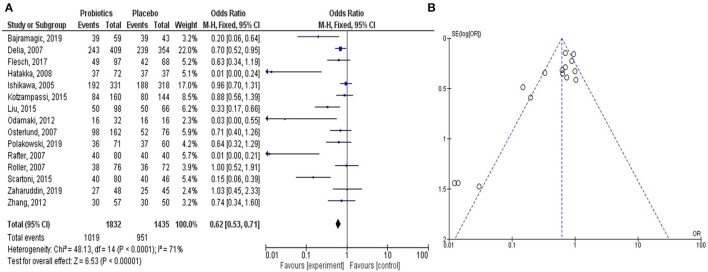
Figure 2.
Meta-analysis study justifies the efficacy of the probiotic intervention in the treatment and prevention of CRC-promoting gut inflammation. The Forest plot shows 95% confidence intervals and pooled mean difference to evaluate the result of placebo controls vs. probiotics-based treatment (after heterogeneity adjustment) on patients with CRC (A). The Funnel plot of the effect size plotted with the standard error examines publication bias to show the effect of probiotics on CRC in various clinical trials (B). The pooled effect size is represented by the perpendicular line to the x-axis. Positive or negative bias is represented by the studies outside the triangle. Thus, the substantial asymmetry in the funnel plot signifies the absence of publication bias.