Figure 3:
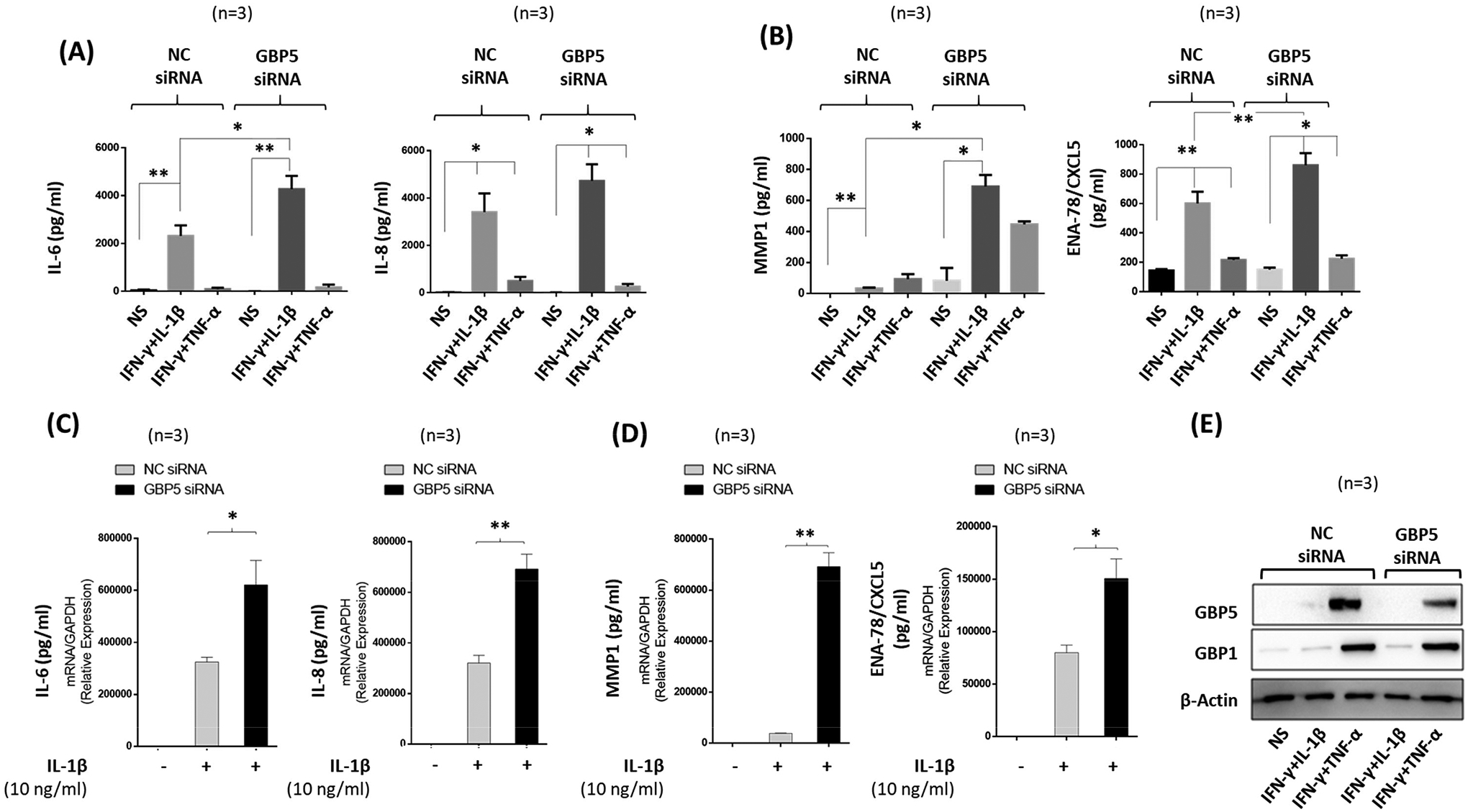
Knockdown of GBP-5 by transient transfection causes loss of IFN-γ protection and further amplifies IL-1β-induced inflammation. A-B, Human RASFs were transfected with scrambled (NC) or GBP-5 siRNA (120 pM) for 48 h followed by serum starvation and stimulation with IFN-γ (10 ng/ml) and IL-1β (10 ng/ml) or TNF-α (20 ng/ml) for 24 h. Knockdown of GBP-5 nullified the effect of IFN-γ and upregulated IL-1β–induced IL-6, IL-8, MMP-1, and ENA-78/CXCL5 production. C-D, RASFs stimulated with IL-1β alone also showed significant increase of IL-6, IL-8, MMP-1, and ENA-78/ CXCL5 mRNA expression in GBP-5 knockdown samples compared to NC samples. E, Western immunoblotting showing the efficiency of GBP-5 knockdown in human RASFs. The values presented in the graphs are mean ±SEM of three independent experiments. *p<0.05 or **p<0.01 vs NS; *p<0.05 or **p<0.01 for NC versus siRNA treatment.
