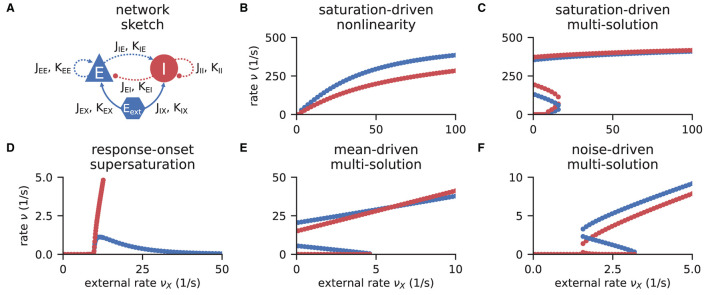
Figure 2.
Response nonlinearities in EI-networks. (A) Network diagram with nodes and edges according to the graphical notation proposed by Senk et al. (in press). (B–F) Firing rate of excitatory (blue) and inhibitory (red) population for varying external input rate νX. Specific choices for synaptic weights (J, Jext) and in-degrees (K, Kext) lead to five types of nonlinearities: (B) saturation-driven nonlinearity, (C) saturation-driven multi-solution, (D) response-onset supersaturation, (E) mean-driven multi-solution, and (F) noise-driven multi-solution. See Figure 8 in Sanzeni et al. (2020) for parameters.