|
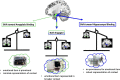
Box 3. Amygdalar and Hippocampal Binding Systems The modulation model proposes that arousal, and specifically norepinephrine release, triggers cooperation between the amygdala and the hippocampus (Roozendaal & McGaugh, 2011). Other research suggests that negative emotion can trigger disconnects between amygdala engagement and hippocampal engagement, consistent with behavioral evidence that negative emotion can lead to memories that are less coherent, with fewer within-event associations (Bisby & Burgess, 2017; Madan et al., 2017; Palombo, Elizur, et al., 2021). For instance, when individuals studied face-occupation pairs, the presence of negative occupations were associated with lower hippocampal engagement during encoding and with poorer memory for those associations (Berkers et al., 2016). Bisby et al. (2016) similarly found that the encoding of negative items was associated with a boost in amygdala activity but with a decrease in hippocampal activity, corresponding with an increase in item memory but a decrease in associative memory for those negative items. Yonelinas and Ritchey’s (2015) Emotional Binding model may provide a framework in which to understand these seemingly conflicting results. By this model, there are two binding systems at work during encoding: an amygdala-based system, that prioritizes binding the item to its emotion, and a hippocampal-based system, that prioritizes binding the item to its context.
It is plausible that there are situations in which both systems are engaged, leading emotional items to be remembered in their broader context, and situations in which it is primarily the amygdala system that is engaged, leading emotional items to be remembered void of their context. An intriguing possibility to be addressed by future research is that negative emotion may create an imbalance between engagement of the amygdala and hippocampal systems and a shift toward amygdala binding, while positive emotion may be more likely to lead to simultaneous engagement of both systems or even a shift toward hippocampal binding. |

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.