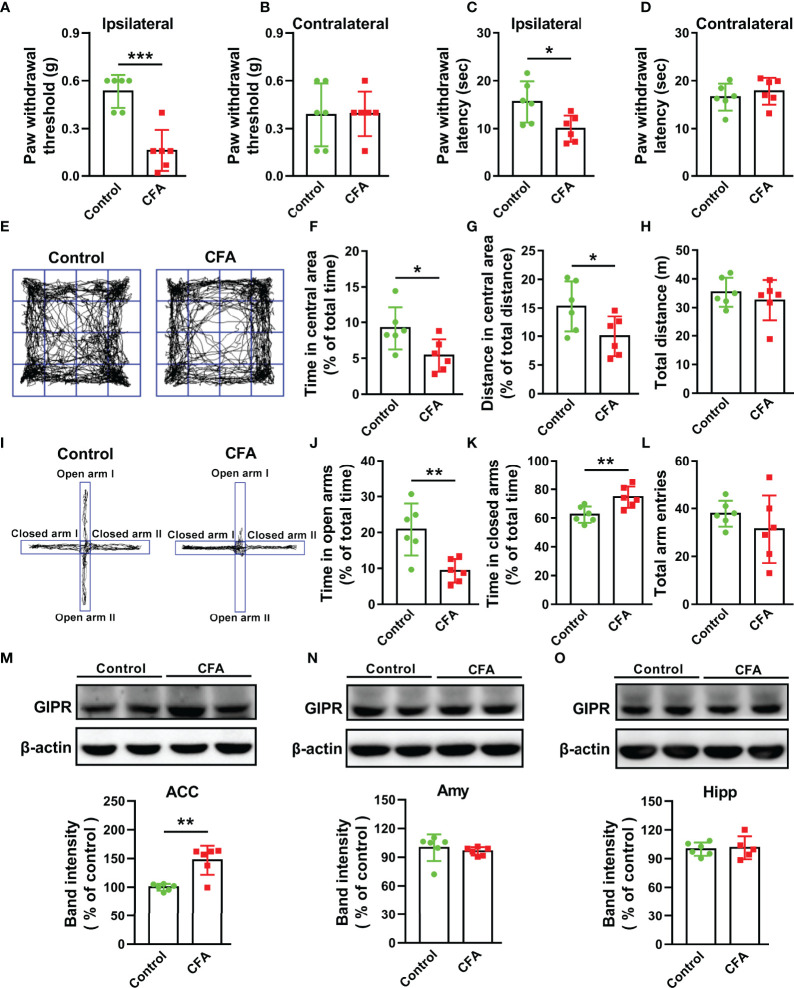
Figure 1.
CFA injection induced nociceptive and anxiety-like behaviors along with the up-regulation of GIPR in the ACC. Paw withdrawal threshold and latency were decreased in CFA-injected paw (ipsilateral) (A, C) but not in non-CFA-injected paw (contralateral) (B, D). (E) Representative traces in OF test. The time spent (F) and distance travelled (G) in the central area but not the total traveled distance (H) were decreased in mice injected with CFA. (I) Representative traces in EPM test. CFA-injected mice spent less time in open arms (J) and more time in closed arms (K) in EPM tests, but had similar total arm entries in open and close arms (L). In CFA-treated mice, GIPR expression significantly increased in the ACC (M), but not in the amygdala (N) and hippocampus (O). n = 6 in each group except for CFA group of Figure 10 (n = 5). Totally, 12 mice were used in this section. Amy means amygdala; Hipp means hippocampus. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.