Figure 1.
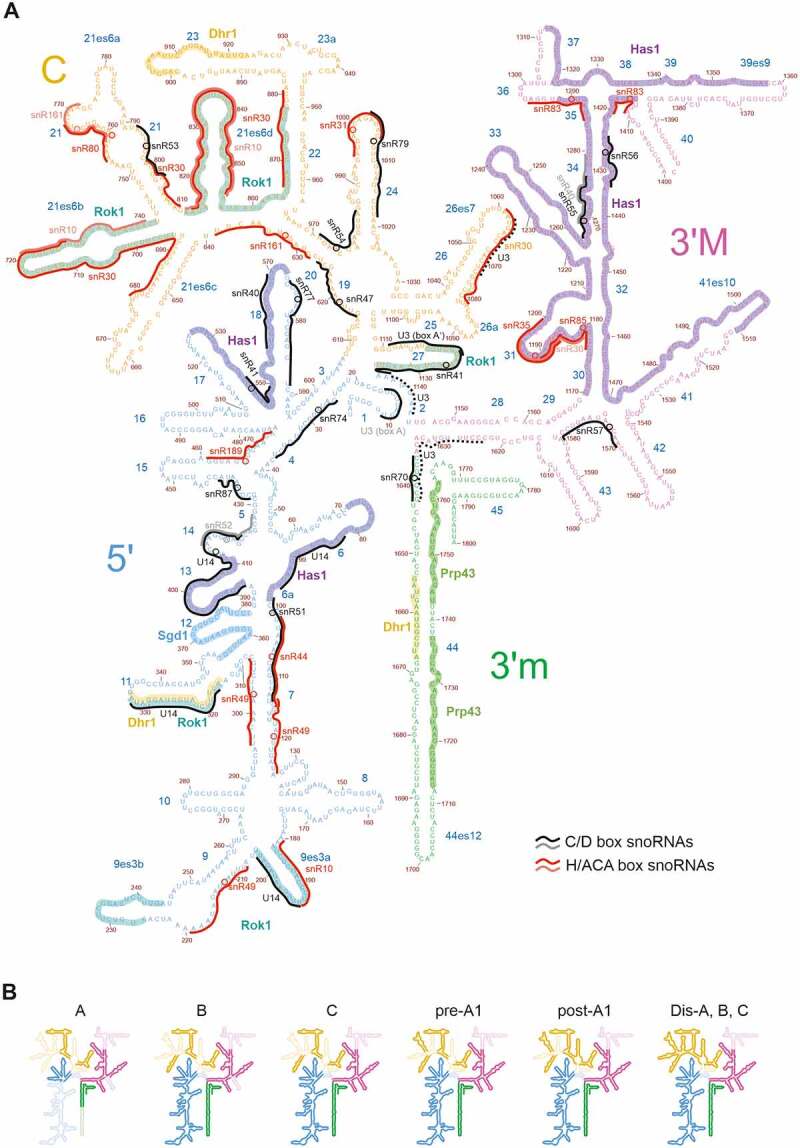
Secondary structure of the 18S rRNA. (A) 18S rRNA with the 5’, central (C), 3’ major (3’M) and 3’ minor (3’m) domains indicated in different colours. All known and predicted snoRNA binding sites [13,19,22,23,114,120,121,129,135] are indicated by black/grey (C/D box) or red/pink (H/ACA box) lines, and modification sites are indicated by circles. In the case of the U3 snoRNA, only the hybridization sites observed in cryo-EM structures are indicated in solid lines, while potential additional hybridization sites suggested by biochemical experiments are indicated as dashed lines. The binding regions of RNA helicases, determined by CRAC, and of the Fal1 helicase cofactor Sgd1 [64,135,178,232,238] are indicated. (B) Successive folding of the 18S rRNA [23]. Already folded rRNA elements are displayed in bright colours (unfolded regions in faint colours).
