Extended Data Fig. 6|. CCR5/CCL5 signaling regulates memory linking in an appetitive place preference task.
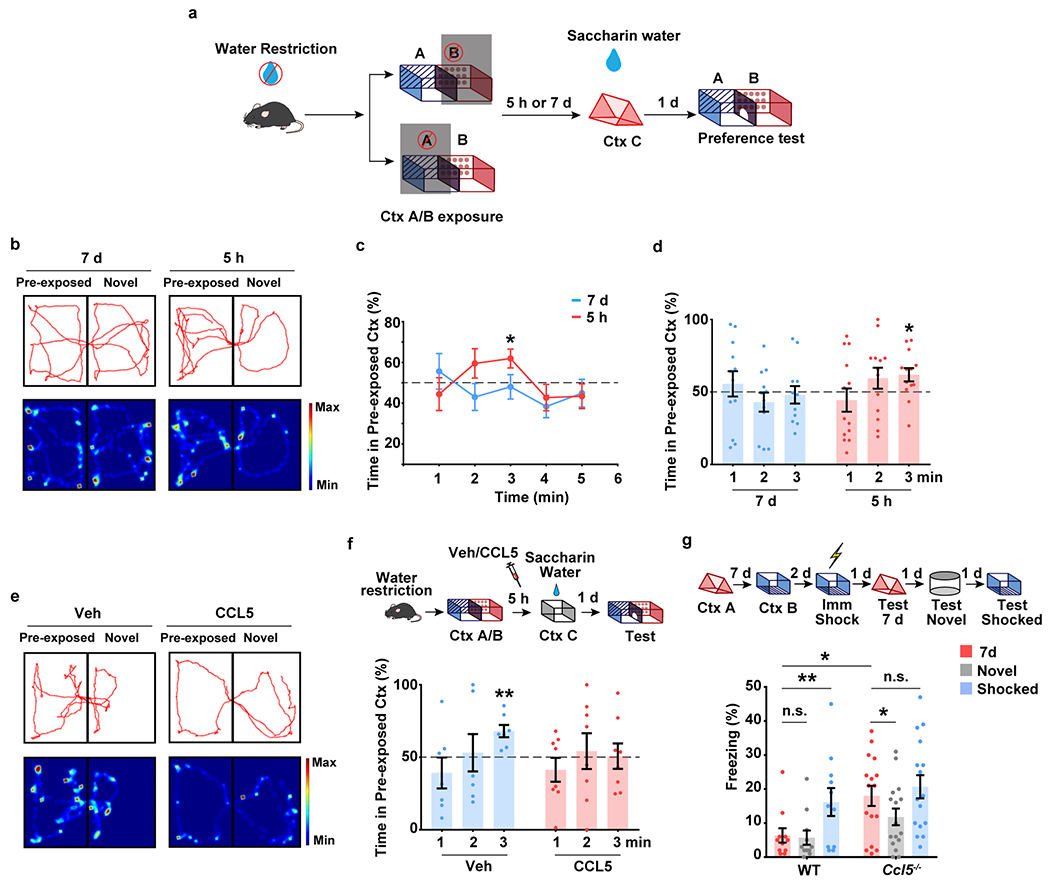
a-f, Place preference-based behavior model to test the linking of contextual memories.
a, Schematics of place preference-based linking behavior.
b, Representative trajectory plot (in the 3rd minute) of mice in the pre-exposed context and a novel context with a 5h and 7d interval.
c, d, Mice showed a significant preference for pre-exposed context during the 3rd minute in the 5h group compared to the 7d group (5h, n=13, 7d n=12 mice; *P < 0.05, one sample paired t-test compared to 50%)
e, Representative trajectory plot (in the 3rd minute) of mice in the pre-exposed context and a novel context with Vehicle or CCL5 infusion.
f, CCL5 infusion in dCA1 impaired contextual memory linking with a 5h interval (Veh n=7, CCL5 n=8; **P < 0.01, one sample paired t-test compared to 50%).
g, Ccl5 knockout extended the temporal window of contextual memory linking (WT n=11, Ccl5−/− n=16; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, two-way repeated measures ANOVA).
All results shown as mean ± s.e.m.
