Fig. 4|. Enhanced CCL5/CCR5 signaling contributes to age-related memory linking deficits.
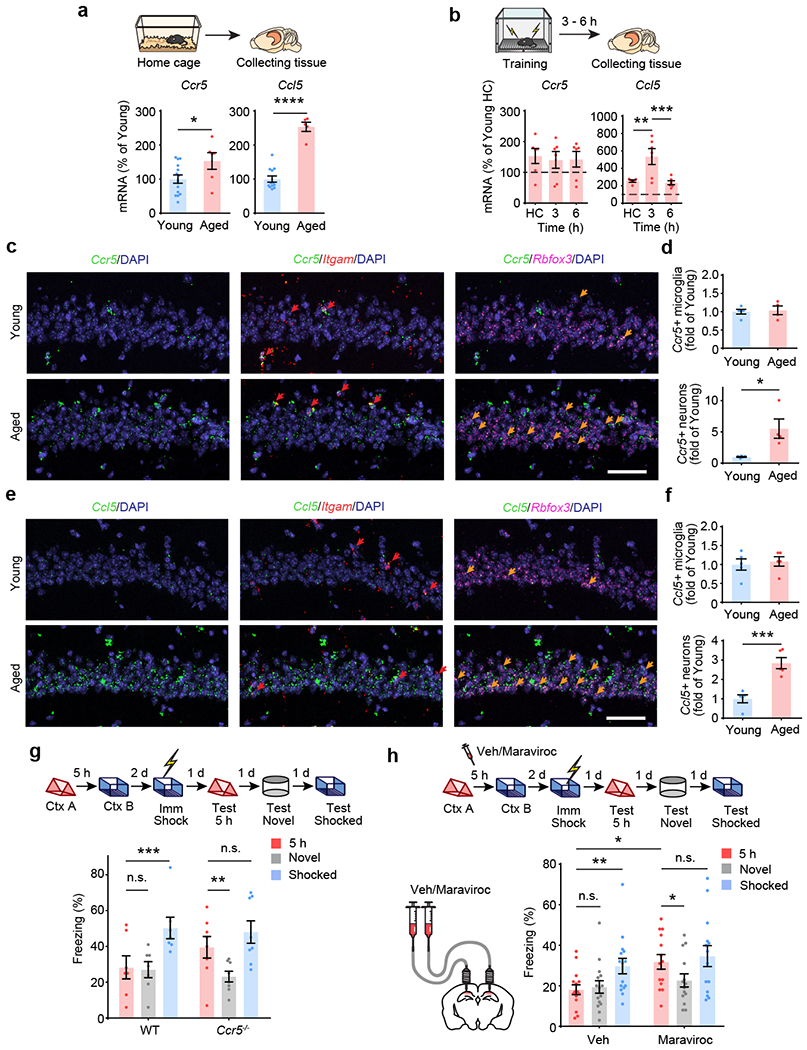
a, Middle-aged HC mice had higher Ccr5 and Ccl5 mRNA levels in dCA1 than young HC mice (Ccr5: young n=14, aged n=6, Ccl5: young n=12, aged n=5; *P < 0.05, ****P < 0.0001, Student’s t-test).
b, Ccr5 and Ccl5 expression after fear conditioning in dCA1 of middle-aged mice (Ccr5: n=6 for all groups, Ccl5: HC n=5, 3h n=6, 6h n=6; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, one-way ANOVA).
c, Representative images of Ccr5, Itgam and Rbfox3 mRNA expression in dCA1 from naïve young or middle-aged mice. Red arrows: cells expressing Ccr5 and Itgam. Orange arrows: cells expressing Ccr5 and Rbfox3. Scale bar, 50 μm.
d, Number of Ccr5-expressing microglia and neurons in young or middle-aged mice (young n=5, aged n=4 mice; *P < 0.05, Student’s t-test).
e, Representative images of Ccl5, Itgam and Rbfox3 mRNA expression in dCA1 from naïve young or middle-aged mice. Red arrows: cells expressing Ccr5 and Itgam. Orange arrows: cells expressing Ccr5 and Rbfox3. Scale bar, 50 μm.
f, Number of Ccl5-expressing microglia and neurons in young or middle-aged mice (n=5 mice; ***P < 0.001, Student’s t-test).
g, Ccr5 knockout rescued 5h memory linking deficits in middle-aged mice (WT n=7, Ccr5−/− n=8; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, two-way repeated measures ANOVA).
h, Maraviroc, a CCR5 antagonist, rescued 5h memory linking deficits in middle-aged mice (Veh n=15, maraviroc n=14; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, two-way repeated measures ANOVA).
All results shown as mean ± s.e.m.
