Extended Data Fig. 5|. Characterization of Opto-CCR5.
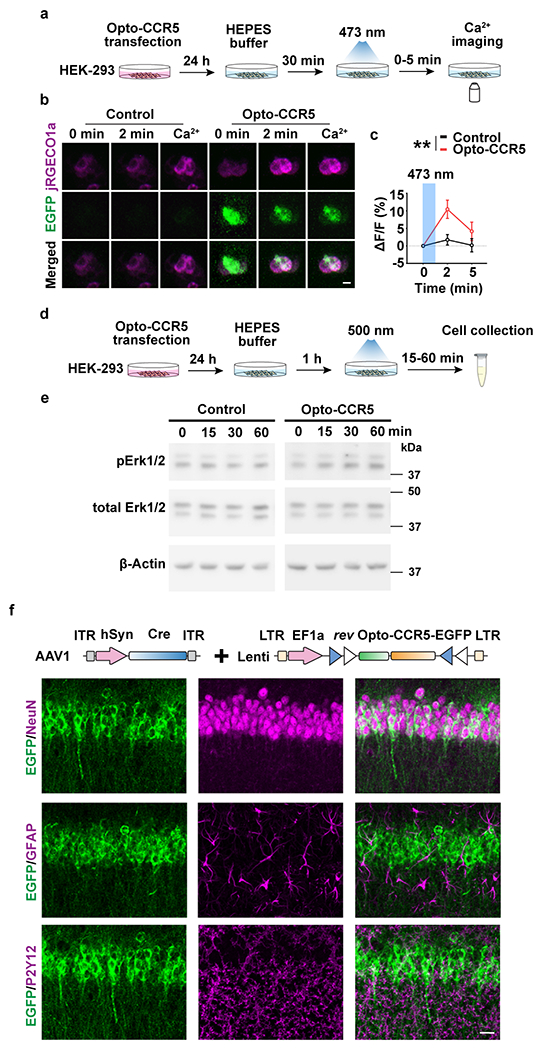
a, HEK-293 cells were transfected with Opto-CCR5 and jRGECO1a (Calcium sensor with red florescence) for 24h and then stimulated with blue light to induce a calcium response.
b, Representative images at 0 min or 2 min after stimulation, or in the medium with high calcium concentration. Scale bar, 20 μm.
c, Quantification of florescence change after light stimulation. In HEK-293 cells, Opto-CCR5-EGFP activation by light significantly increased intracellular Ca2+ concentration reflected by jRGECO1a (Control 2 min n=95, Control 5 min n=96, Opto-CCR5 2 min n=86, Opto-CCR5 5 min n=89 cells; **P < 0.01, two-way ANOVA).
d, e, Opto-CCR5 activation increased pErk1/2 in HEK-293 cells.
d, HEK-293 cells were transfected with the Opto-CCR5 construct. After 24h expression, the cells were starved in HEPES buffer for 1h before a 2 min light stimulation to reduce basal pErk1/2 levels. Cells were collected at 0 (no light stimulation), 15, 30 or 60 min after light stimulation and subjected to Western blot analysis to investigate the phosphorylation level of Erk1/2 (e).
f, Expression of Opto-CCR5 in dCA1 neurons. To express Opto-CCR5 in dCA1 neurons, AAV1-hSyn-Cre was co-injected with Lenti-DIO-Opto-CCR5. NeuN (neuron marker), GFAP (astrocyte marker) and P2Y12 (microglia marker) were co-stained with EGFP in dCA1. Scale bar, 20 μm.
All results shown as mean ± s.e.m.
