Figure 2. Molecular barcoding for NGS libraries to improve detection of rare mutations.
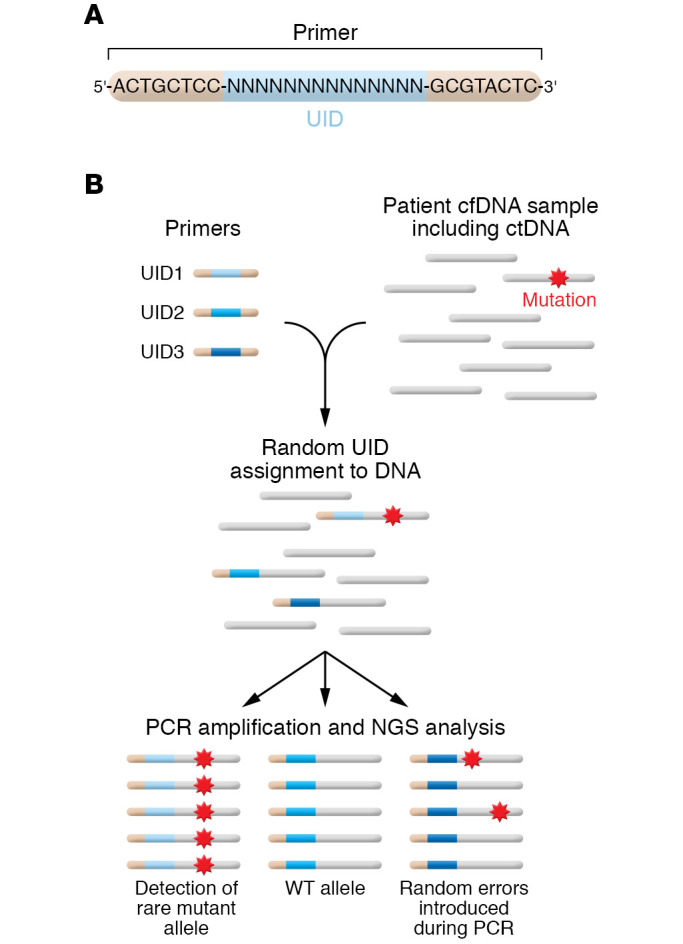
(A) Incorporation of random sequences for degenerate primers used to molecularly tag each DNA molecule. Each “N” can be either A, C, G, or T and is chosen randomly during synthesis. (B) Schema of Safe-SeqS (adapted with permission from Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA; ref. 84). Clinically relevant mutations are present at very low frequency in patient samples. Barcoding of DNA can improve the signal-to-noise ratio in NGS analysis, because mutant tumor alleles containing the same UID will be amplified, whereas random errors resulting from PCR amplification will remain at low frequency.
