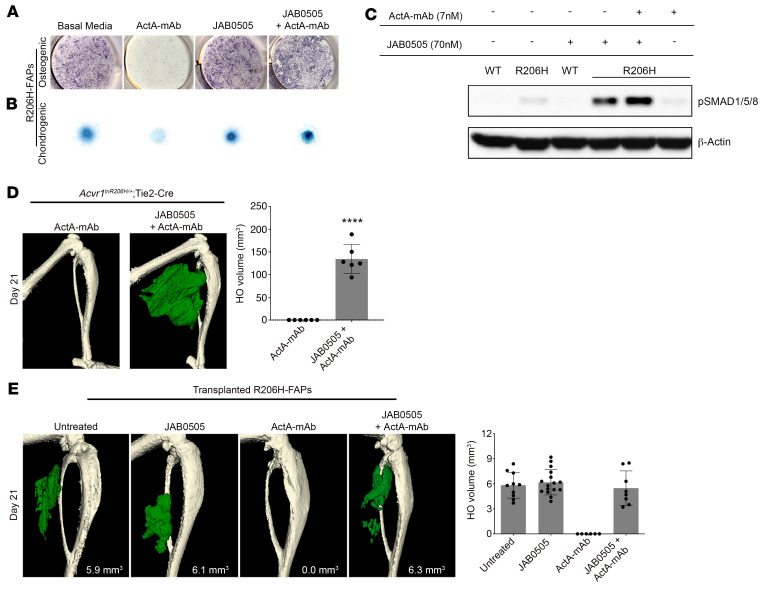
Figure 5. JAB0505 functions as an agonist of ACVR1(R206H).
(A) Osteogenic differentiation of monolayer R206H-FAP cultures, as assessed by ALP staining (purple), and (B) chondrogenic differentiation of micromass cultures assessed by Alcian blue staining. ActA-mAb was used at 1 μg/mL (7 nM) and JAB0505 was used at 10 μg/mL (~70 nM). (C) Western blot of phosphorylated SMAD1/5/8 (p-SMAD1/5/8) in wild-type (WT) and R206H-FAPs (R206H). β-Actin was used as a loading control. (D) μCT of the distal hind limb of Acvr1tnR206H/+; Tie2-Cre mice on day 21 after injury. At the time of muscle injury, mice were treated with ActA-mAb (10 mg/kg) alone or ActA-mAb with JAB0505 (10 mg/kg). HO is pseudocolored green, and quantification is shown. ActA-mAb, n = 6; JAB0505 plus ActA-mAb, n = 6. Error bars represent ±SD. ****P < 0.0001 by 2-tailed, unpaired t test. (E) μCT images of the distal hind limb 21 days after transplantation of R206H-FAPs into the injured gastrocnemius of SCID hosts. ActA-mAb (10 mg/kg) and JAB0505 (10 mg/kg) were administered at the time of transplantation. HO is pseudocolored green and quantified, with error bars representing ±SD. Untreated, n = 10; JAB0505, n = 16; ActA-mAb, n = 6; JAB0505 plus ActA-mAb, n = 8.