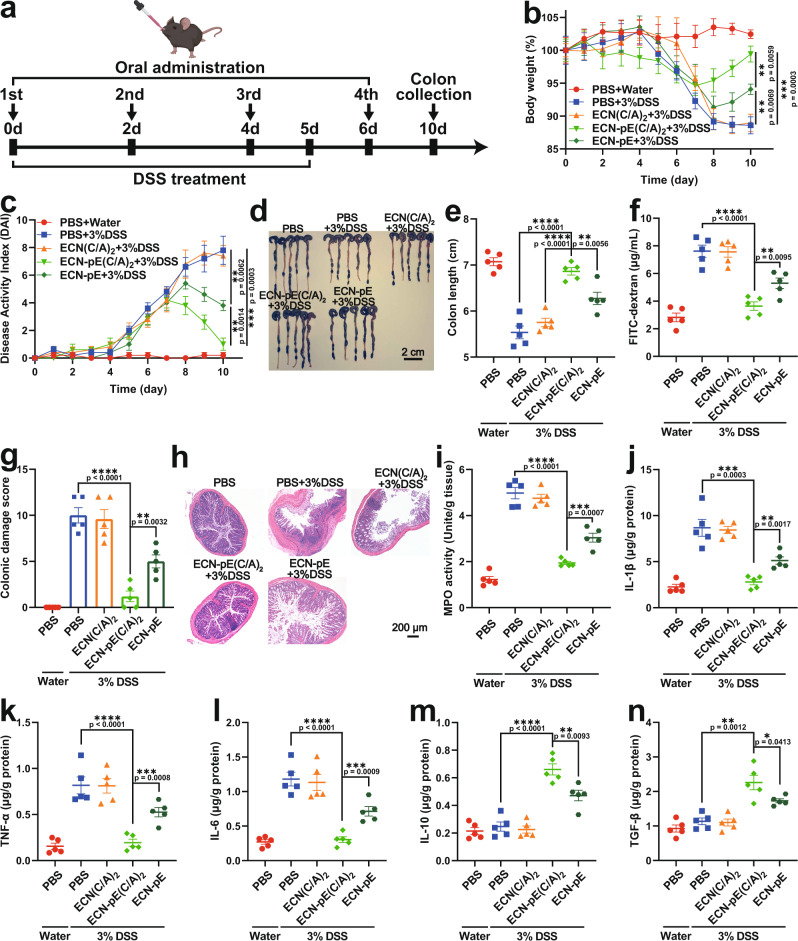
Fig. 3. Treatment efficacy of ECN-pE(C/A)2 against DSS-induced murine IBD.
a Schematic showing the experimental procedure for the treatment of DSS-induced IBD mice. C57BL/6 mice were given drinking water containing 3% DSS from day 0 to day 5. Meanwhile, the mice were fed PBS, ECN(C/A)2, ECN-pE(C/A)2 or ECN-pE (1 × 108 CFU) on days 0, 2, 4, and 6 by gavage. b The body weight of the mice with different treatments. c The DAI of mice during the treatment. d Photographs and (e) corresponding quantified lengths of colons harvested from mice 10 days after different treatments. Scale bar: 2 cm. f The intestinal integrity function of mice was assessed by FITC-dextran assay after different treatments. g The colonic damage scores of mice after different treatments. h Representative images of H&E staining of colon tissue harvested on day 10 after different treatments from five biologically independent animals in each group. Scale bar: 200 μm. i The MPO activity in the colons of mice after different treatments. MPO, myeloperoxidase. j–n The levels of IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-10, and TGF-β in the colon tissues measured by ELISA on day 10. Data are presented as mean values ± SEM (n = 5 biologically independent samples for (b, c, e–g, and i–n)). Statistical analysis was evaluated with two-tailed Student’s t tests (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 00001). DSS dextran sodium sulfate. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.