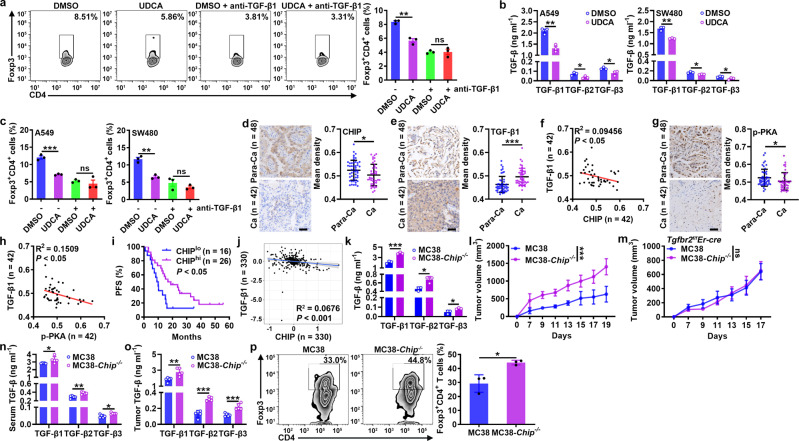
Fig. 6. CHIP inhibits tumor progression by reducing the TGF-β level.
a FC analysis of Foxp3+CD4+ T cells among human naïve CD4+ T cells stimulated with anti-CD3, anti-CD28 and 50 μM UDCA with or without 2 μg ml−1 anti-TGF-β1 for 4 days. b ELISA of TGF-β1, TGF-β2 and TGF-β3 proteins in supernatants of A549 and SW480 cells treated with 50 μM UDCA for 24 h. c FC analysis of Foxp3+CD4+ T cells among human naïve CD4+ T cells stimulated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 with or without 2 μg ml−1 anti-TGF-β1 and cultured in the supernatants described in b for 4 days. d–h Immunohistochemical analysis of CHIP (d), TGF-β1 (e) and p-PKA (g) in Para-Ca tissues and Ca tissues (d, e, g) and correlations between CHIP and TGF-β1 (f), p-PKA and TGF-β1 (h) protein levels in Ca tissues (f, h) of NSCLC patients. i PFS curve for NSCLC patients with low versus high CHIP protein levels. j Correlation between CHIP and TGF-β1 protein levels in Ca tissues of HCC patients from the CPTAC database. k ELISA of TGF-β1, TGF-β2, and TGF-β3 proteins in the supernatants of MC38 and MC38-Chip−/− cells. l-p Tumor sizes in MC38 and MC38-Chip−/− tumor-bearing WT (l) and Tgfbr2f/fEr-cre (m) mice. ELISA of TGF-β1, TGF-β2 and TGF-β3 proteins in serum (n) and tumor tissues (o) and FC analysis of Foxp3+CD4+ T cells among TILs (p) from MC38 and MC38-Chip−/− tumor-bearing mice on day 7 (n, o) and on day 19 (p). Representative results from three independent experiments are shown (n = 3 in (a–c, k, p); n = 5 in l-o). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ns, not significant (unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test in (a–e, g, k–p); Spearman rank-order correlation test in f, h, j; log-rank test in i; mean and s.d.). See Source Data file for the exact P-values.