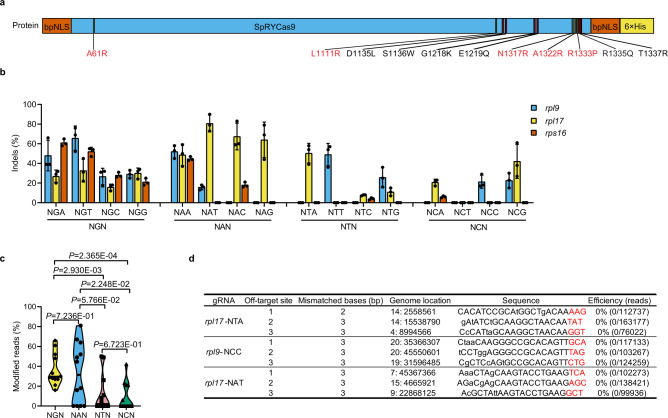
Fig. 2. Optimized SpRYCas9 nuclease targeted different NNN PAMs in zebrafish.
a Schematic illustration of the amino acid mutations that developed SpRYCas9 from SpGCas9. Five more amino acid mutations (A61R, L1111R, N1317R, A1322R, and R1333P; in red) were introduced into SpGCas9 to obtain SpRYCas9. b The editing efficiency of 48 gRNAs targeting NNN PAMs of rpl9, rpl17, and rps16 in zebrafish. (Values are presented as mean value ± standard deviation (SD), n = 3 biological replicates). c Assessment of the preference of SpRYCas9-mediated mutagenesis for the second N of NNN PAMs using the violin plot based on the data in b, Each data point represents the averaged editing activity at the particular site. The centre line shows means of all data points. Two-tailed paired t test were performed (with P values marked). d Detection of mutation at potential off-target sites induced by SpRYCas9 nuclease at three loci using NGS. The PAM sequences are underlined in red. All source data in this figure are provided as a Source data file.