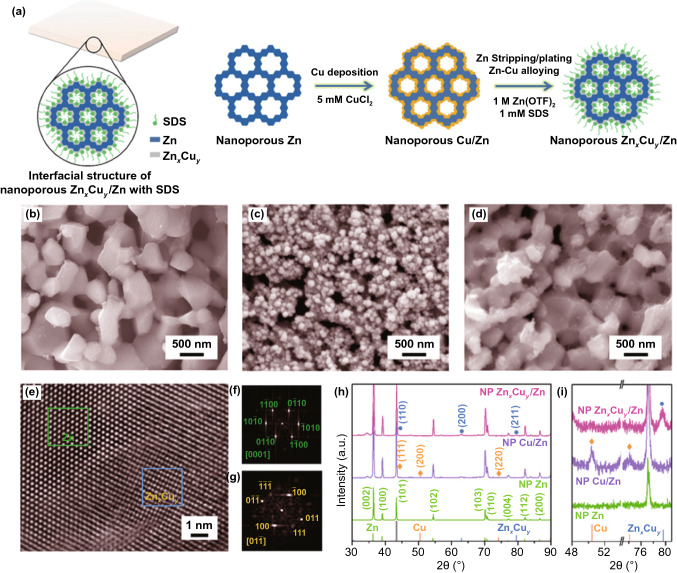
Fig. 1.
Schematic and microstructural properties of nanoporous Zn-based electrodes. a Schematic illustration for nanoporous shell/core ZnxCuy/Zn sheets that are fabricated by surface alloying of Cu and Zn of Cu-decorated nanoporous Zn during sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-assisted electrochemical Zn stripping/plating cycling. b SEM image of nanoporous Zn electrode that is prepared by chemically dealloying Zn50Al50 alloy sheets in KOH solution. c SEM image of nanoporous Cu/Zn hybrid electrode, in which Cu nanoparticles with diameter of ~ 50 nm are deposited on surface of nanoporous Zn skeleton via a galvanic replacement reaction. d SEM image of surface-alloyed nanoporous ZnxCuy/Zn electrode after SDS-assisted Zn stripping/plating in Zn(OTF)2 for 10 cycles. e HRTEM image of ZnxCuy/Zn interface of nanoporous ZnxCuy/Zn electrode. f, g FFT patterns of HCP Zn (f) and cubic ZnxCuy (g) phases corresponding to green and blue squares in e. h Typical XRD patterns of nanoporous Zn, Cu/Zn and ZnxCuy/Zn electrodes. The line patterns show reference cards 65-3358 and 85-1326, 02-1231 for monometallic Zn and Cu, ZnxCuy alloy according to JCPDS, respectively. i A magnification of XRD patterns of nanoporous Zn, Cu/Zn and ZnxCuy/Zn electrodes at the characteristic diffraction peak regions of monometallic Cu and ZnxCuy alloy