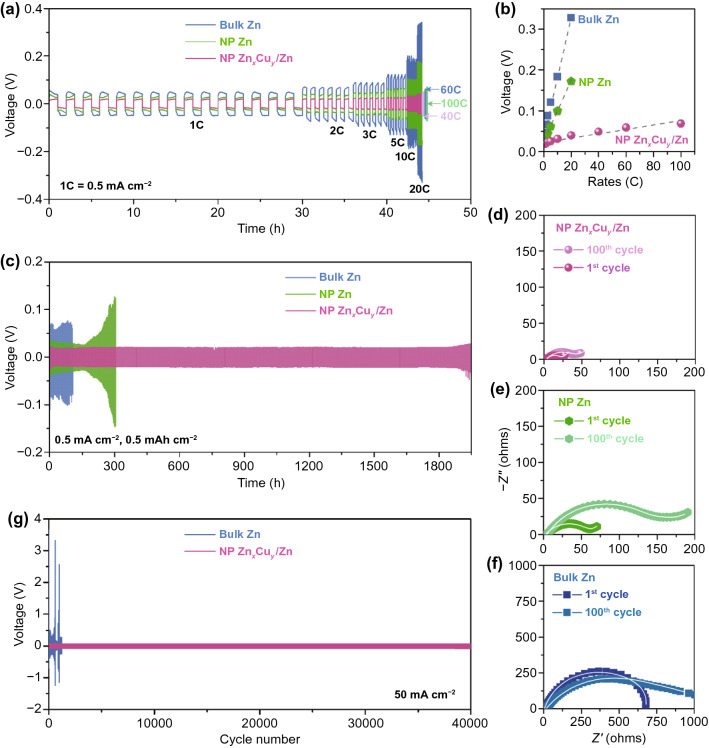
Fig. 3.
Electrochemical performance of symmetric cells. a Voltage profiles of nanoporous ZnxCuy/Zn symmetric cell at various rates from 1 to 100C (1C = 0.5 mA cm‒2) in 1 M Zn(OTF)2 with 1 mM SDS, comparing with those of symmetric batteries of bulk Zn and nanoporous Zn electrodes in 1 M Zn(OTF)2. b Overpotentials of Zn stripping/plating for symmetric cells based on nanoporous ZnxCuy/Zn and nanoporous Zn, bulk Zn in 1 M Zn(OTF)2 with/without 1 mM SDS as a function of rate. c Long-term cycling stability of Zn stripping/plating for symmetric cells based on nanoporous ZnxCuy/Zn and nanoporous Zn, bulk Zn in 1 M Zn(OTF)2 with/without 1 mM SDS.EIS spectra of d nanoporous ZnxCuy/Zn, e nanoporous Zn and f bulk Zn symmetric cells before and after 100 cycles of stripping/plating in 1 M Zn(OTF)2 with/without 1 mM SDS. g Long-term Zn stripping/plating stability of symmetric cells based on nanoporous ZnxCuy/Zn and bulk Zn electrodes in 1 M Zn(OTF)2 with/without 1 mM SDS at 50 mA cm‒2, respectively