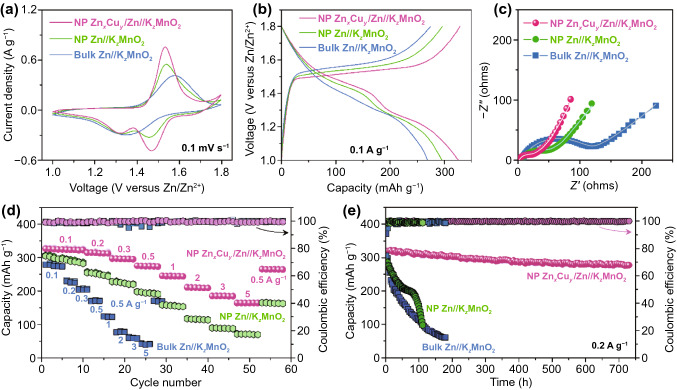
Fig. 4.
Electrochemical performance of full Zn-ion cells. a Representative CV curves of full cells of nanoporous ZnxCuy/Zn//KzMnO2, nanoporous Zn//KzMnO2 and bulk Zn//KzMnO2. Scan rate: 0.1 mV s‒1. b Representative charge/discharge voltage profiles of nanoporous ZnxCuy/Zn//KzMnO2, nanoporous Zn//KzMnO2 and bulk Zn//KzMnO2 full cells at the specific current of 0.1 A g‒1 (based on the loading mass of electroactive KzMnO2 at the cathode). c EIS spectra of nanoporous ZnxCuy/Zn//KzMnO2, nanoporous Zn//KzMnO2 and bulk Zn//KzMnO2 full cells. d Comparisons of rate performance and coulombic efficiency for nanoporous ZnxCuy/Zn//KzMnO2, nanoporous Zn//KzMnO2 and bulk Zn//KzMnO2 full cells, where are performed at various specific currents from 0.1 to 5 A g‒1. e Capacity retentions and coulombic efficiencies of nanoporous ZnxCuy/Zn//KzMnO2, nanoporous Zn//KzMnO2 and bulk Zn//KzMnO2 full cells in a long-term charge/discharge cycling measurements at the specific current of 0.2 A g‒1