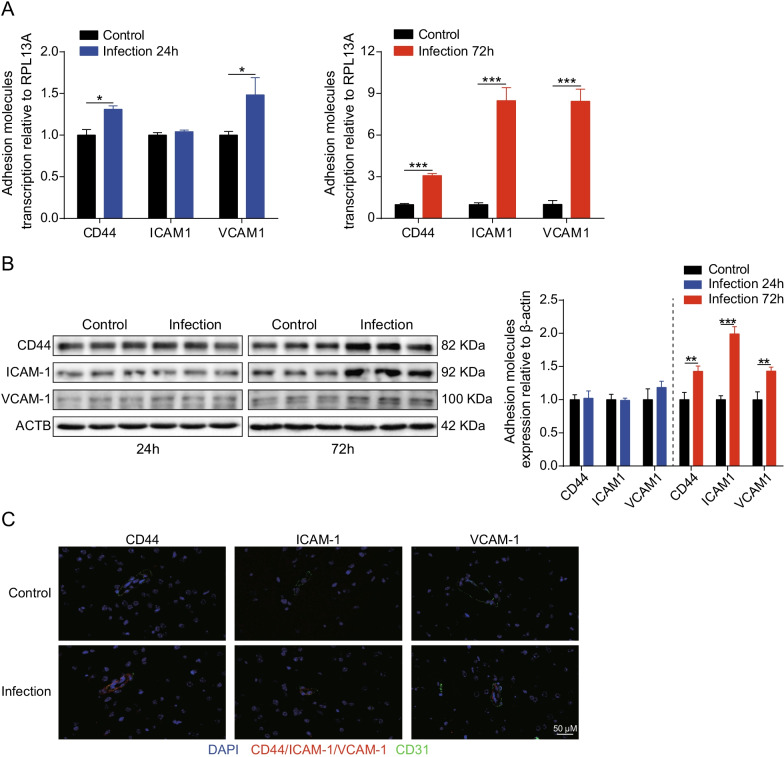
Fig. 5.
SARS-CoV-2 infection increases expression of adhesion molecules in vitro and in vivo. A RT-qPCR analysis of CD44, ICAM1, and VCAM1 transcription in hBMECs 24 and 72 h post-SARS-CoV-2 infection. RPL13A was used as the internal reference. Data were presented as the mean ± SD from three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001. B Western blot analysis of CD44, ICAM1, and VCAM1 in hBMECs in response to SARS-CoV-2 after 24 and 72 h. β-Actin was used as the loading control, and differences were analyzed by densitometry. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. C Brain samples of both mice infected with SARS-CoV-2 for 5 d and those without were analyzed for the expression of adhesion molecules by immunofluorescence. The CD44, ICAM1, and VCAM1 were selected as the markers reflecting the expression of adhesion molecules in red. CD31 was specifically applied for labeling the micro-vessels in green. The cell nucleus was stained in blue with DAPI. Scale bar indicates 50 μm