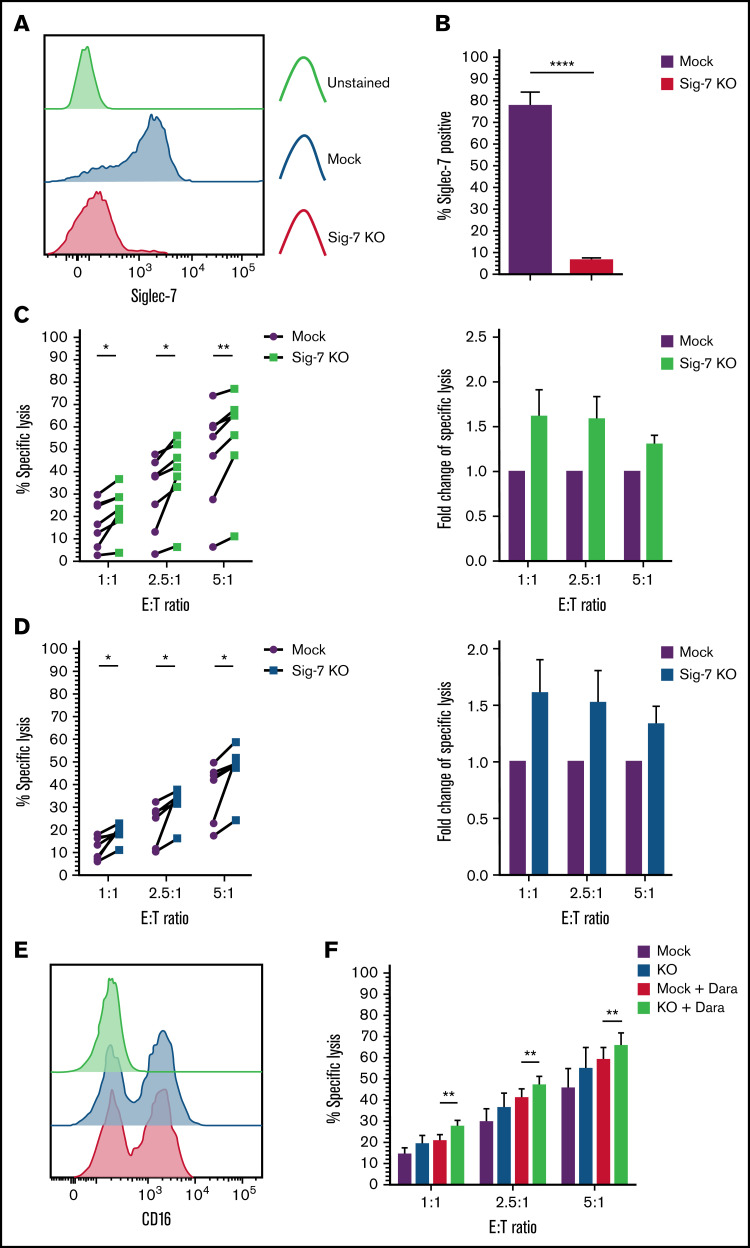
Figure 7.
Targeted knockout of Siglec-7 using CRISPR/Cas9 enhances NK cell–mediated cytotoxicity toward Siglec-7L+/CD38+ MM cell lines. Siglec-7 was targeted for KO using the CRISPR/Cas9 system and the MaxCyte GT transfection system. NK cells were isolated and expanded from peripheral blood of healthy donors for 10 to 14 days prior to transfection. Cytotoxicity assays using CRISPR/Cas9-targeted NK cell were carried out 6 to 9 days after transfection. Siglec-7 KO was determined using flow cytometry, and efficiency was analyzed and displayed as a histogram (A) representative of n = 1 Siglec-7 KO readout on viable NK cells and bar graphs (B) of mock electroporated and CRISPR-targeted NK cells representing complete KO of Siglec-7 in n = 7 donors. Functionality of Siglec-7 KO NK cells was measured in cytotoxicity assays against the Siglec-7L+ MM cell lines H929 (C) and JJN3 (D). (E) CD16 expression was recorded on Mock and Siglec-7KO NK cells using flow cytometry. (F) Mock and Siglec-7KO NK cells were cocultured with Dara-treated CD38+ MM1S MM cells in cytotoxicity assays. Cytox assays were carried out for 4 hours; graphs represent mean specific lysis + SEM. n = 7 biological replicates (B-C); n = 6 (F). (B-D) Data analyzed using Student’s paired t-test; (F) data analyzed using one-way ANOVA. (C-D) Data represent individual values recorded in n = 7 biological replicates and fold change in specific lysis by both mock and Siglec-7KO NK cells. *P < .05; **P < .01; ****P < .0001.