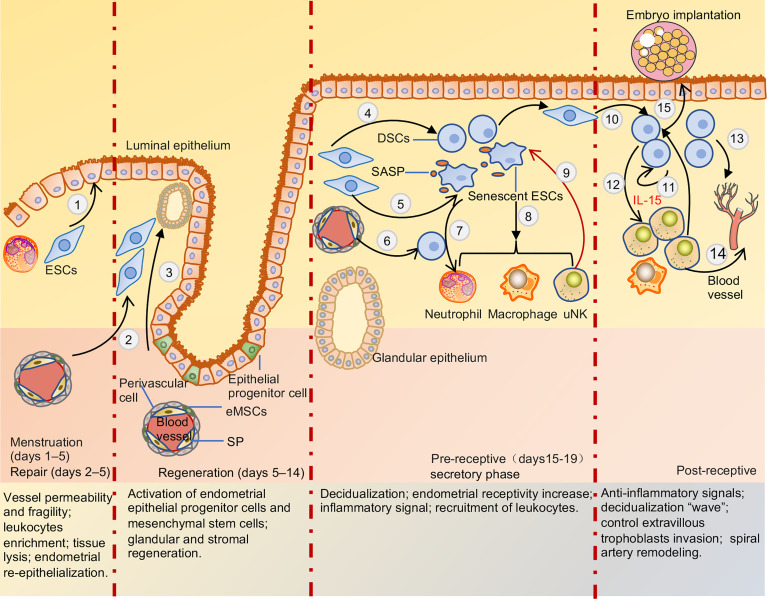
Figure 2.
Menstruation cycle and pre-receptive and post-receptive endometrium. When the embryo is not explanted, DSCs secrete multiple chemokines that drive inflammatory cells into endometrial due to hormone withdrawal, recruitment of leukocyte increased activation and production of proteolytic enzymes, enhance reactive oxygen species release, and inhibition of superoxide dismutase activity, leading to tissue destruction and lysis. Post-menstrual repair of endometrium mainly depends on epithelium migration and endometrial stromal cells differentiation (1) to facilitate re-epithelialization and terminate bleeding. Regeneration of the endometrium is mainly mediated by endometrial epithelial progenitor cells and perivascular mesenchymal stem cells differentiation glands and stroma respectively (2,3). After ovulation, endometrial stromal cells and mesenchymal stem cells can be transformed into decidua stromal cells due to the withdrawal of estrogen and progesterone (4,6). Endometrial stromal cells also can be transformed into senescent decidual cells in the process of decidualization (5). Cytokines secreted by decidua stromal cells and SASP released by senescent decidual cells recruited leukocytes into functional layers to maintain a pro-inflammation environment (7,8). uNK cells can clear senescent decidual stromal cells and terminal differentiation of decidual cells, support the conversion of endometrial pro-inflammatory signals to anti-inflammatory signals, and facilitate embryo adhesion (9). After the embryo is implanted, decidual stromal cells generate a ‘wave’ of decidualization by autocrine and paracrine cytokines and spread throughout the uterus (10,11). And decidual stromal cells significantly induce uNK cells proliferation and differentiation by secreting IL-15 (12). Multiple cytokines and angiogenic factors secreted by decidua stroma cells, uNK cells, and macrophage cells induce uterine spiral arteries to remodel (13,14). Meanwhile, uNK cells and decidual stromal cells can control EVT cells invasion and sense embryo quality (15). ESCs, endometrial stromal cells; eMSCs, endometrial mesenchymal stem cells; SP, side-population cells; DSCs, decidua stromal cells; SASP, senescence-associated secretory phenotype; uNK, uterine natural killer cell.