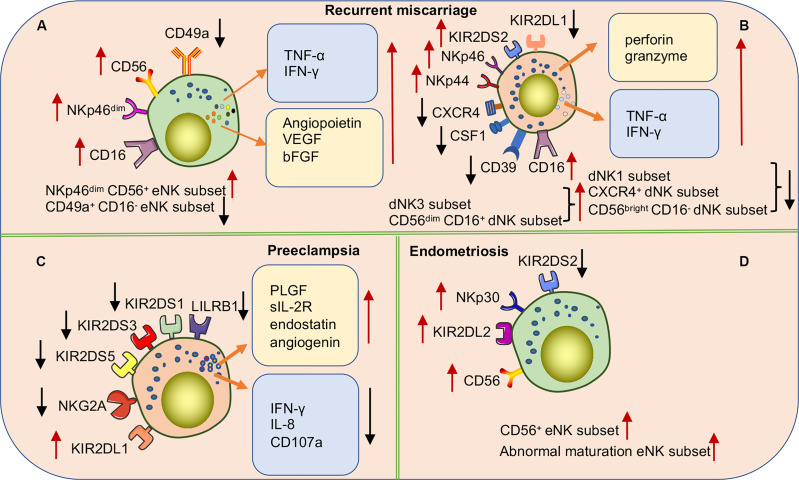
Figure 6.
Subpopulations or functional alterations of human uNK cells in pregnancy complications. (A) NKp46dim CD56+ eNK cell populations in RM patients are significantly increased while the CD49a+ CD16- eNK cell populations significantly decrease. In addition, there are a significant accumulation of various cytokines in eNK cells. (B) In women with RM, the expression of various NCRs and activating receptor KIR2DS2 is up-regulated, and the inhibitory receptor KIR2DL1 is down-regulated to activate dNK cells. The frequencies of dNK1 cell, CXCR4+ dNK cell, and CD56bright CD16- dNK cell subsets are significantly decreased while dNK3 cells and CD56dim CD16+dNK cell subsets significantly increased. (C) The cytokine secretion profile of dNK cells is markedly altered in preeclampsia patients. Downregulation of activating receptor expression on the surface of NK cells or upregulation of inhibitory receptors inhibits NK cell activation causing a high risk of developing PE. Especially when maternal NK cells carrying the KIR AA genotype are combined with embryos carrying the HLA-C2 gene. (D) In women with endometriosis, higher frequencies of CD56+eNK cells and abnormal maturation eNK cells are found in eutopic endometrium. Upregulation of inhibitory receptors or downregulation of activating receptors leads to over suppression of eNK cell function associated with the occurrence and severity of endometriosis.