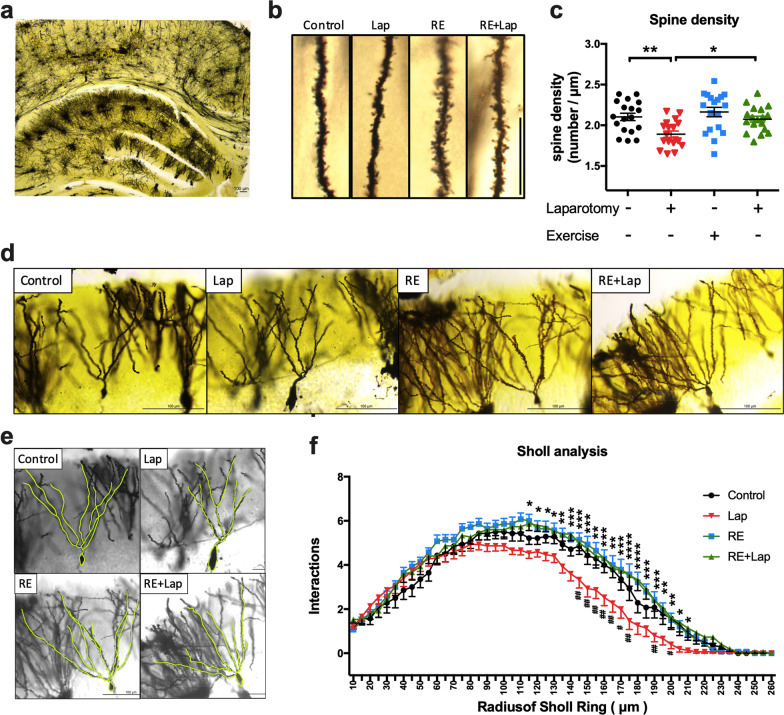
Fig. 3.
Resistance training attenuated the synaptic deficiency in aged mice following surgery. a A representative photograph of Golgi staining of the hippocampus. b Representative pictures of dendritic spines for the four experimental groups. The spine density is significantly decreased in the lap compared with control. c Quantitative analysis of spine density for the four experimental groups. An increase in spine density was observed in the laparotomy group with RE training compared with laparotomy only group. Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey multiple comparisons test, n = 18 in total, 4–5 dendrites were chosen at random from 4 mice in each group. d–f Sholl profiles generated with semi-automated analyses revealing process complexity of dendrites. Significant increases in branch points 120 μm proximal to the cell body layer from laparotomy group with RE training when compared with laparotomy group in areas. Data were analyzed by repeated-measures two-way ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni test as post hoc comparisons, n = 14–15 in total, 3–4 neurons were chosen from 4 mice in each group. Data were presented as mean ± SEM, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001, resistance exercise before laparotomy (RE + Lap) versus laparotomy (Lap) group. #p < 0.05 and ##p < 0.01 Control versus laparotomy (Lap)