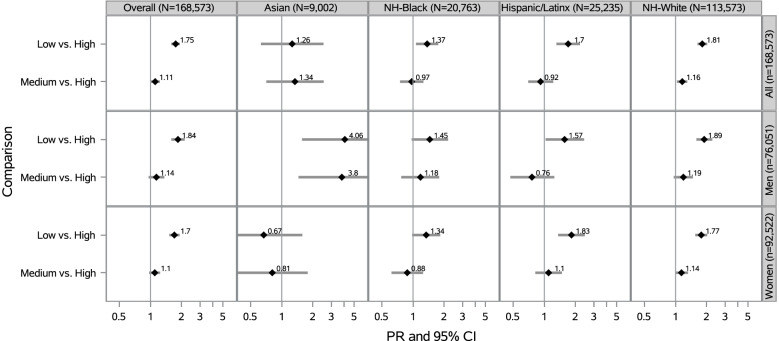
Fig. 3.
Prevalence Ratios of SPD by nSC, Overall and Stratified by Race/Ethnicity and Sex/Gender (N = 168,573). PR = Prevalence Ratio; CI = Confidence Interval; Adjusted for age (18–30, 31–49, ≥ 50 years), educational attainment (< high school, high school graduate, some college, ≥ college), annual household income (< $35,000, $35,000-$74,999, $75,000 +), occupational class (professional/management, support services, laborers), region of residence (Northeast, Midwest, South, West), alcohol consumption (never, former, current), “ideal” cardiovascular health (never smoking/quit > 12 months prior to interview, BMI 18.5- < 25 kg/m2, meeting physical activity guidelines, and no prior diagnosis of dyslipidemia, hypertension, or diabetes/prediabetes), marital/co-habiting status (married/living with partner or cohabitating, divorced/widowed/separated, single/no live-in partner), employment status (unemployed, employed), and self-rated health status (excellent/very good, good, fair/poor). All model additionally adjusted for sex/gender (woman, man). Overall models adjusted for race/ethnicity (NH-White, NH-Black, Hispanic/Latinx, and Asian). Note. All estimates are weighted for the survey’s complex sampling design. Interaction results between nSC*race/ethnicity were significant (p-value < 0.05) and interaction results between nSC*sex/gender were not statistically significant