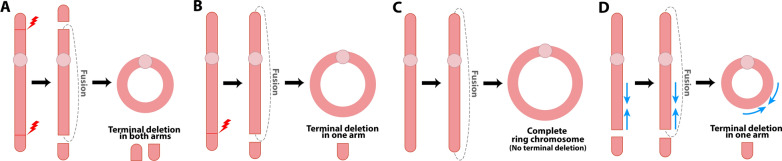
Fig. 8.
Ring Chromosome Formation. A Two terminal double-strand breaks in each chromosome arm and subsequent fusion of the broken ends lead to the formation of a ring chromosome with terminal deletions in both arms. B A terminal double-strand break in one arm and subsequent fusion of the broken end with the opposite arm's telomeric or subtelomeric region leads to the formation of a ring chromosome with terminal deletions in one arm. C Fusion of the telomeric or subtelomeric regions of a chromosome without terminal deletions leads to the formation of a complete ring chromosome. D An inv dup del chromosome can be stabilized via circularization after fusion of the end of the inverted duplication with the opposite arm's telomeric or subtelomeric region, leading to the formation of a ring chromosome with inverted duplication (blue arrows) and terminal deletion