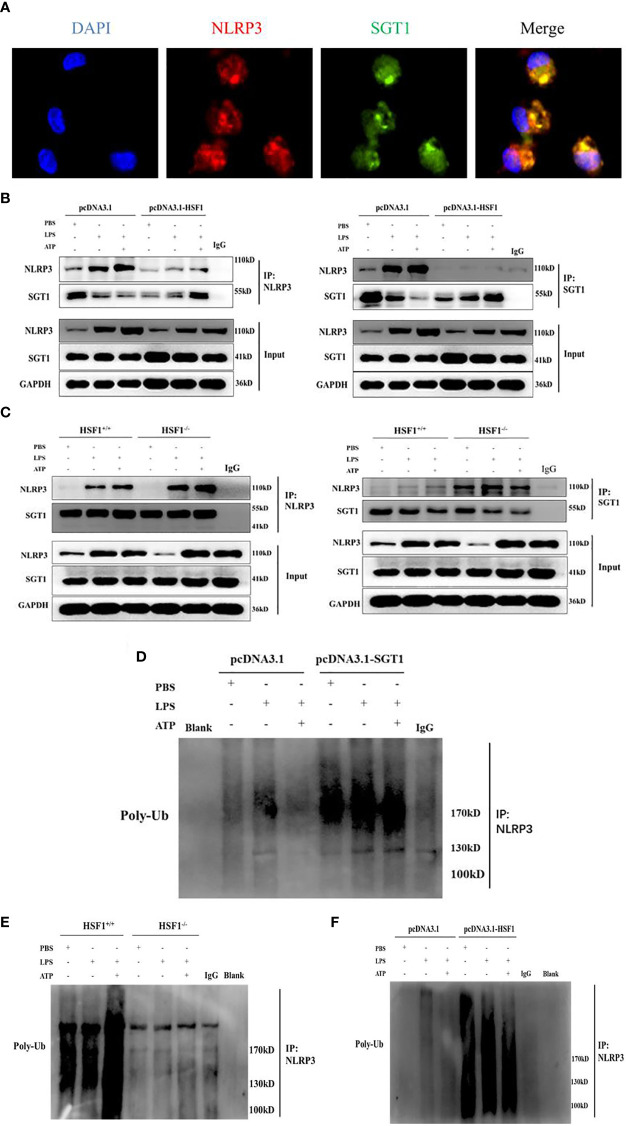
Figure 6.
HSF1 inhibited the NLRP3 inflammasome activation by increasing the ubiquitination of NLRP3. (A) Expression and localization of NLRP3 and SGT1 in primary peritoneal macrophages were detected by immunofluorescence. Green and red colors represent SGT1 and NLRP3, respectively; blue represents nuclei. Merge (yellow) in the overlay images indicates co-localization. (B) The effects of HSF1 overexpression on the interaction between NLRP3 and SGT1 in LPS3h (1 μg/ml) and ATP (5.0 mM) induced RAW264.7 cells. (C) The effects of HSF1 knockout on the interaction between NLRP3 and SGT1 in LPS3h (100 ng/ml) and ATP (2.5 mM) induced primary peritoneal macrophages. (D) The effect of SGT1 overexpression on the ubiquitination of NLRP3 in LPS3h (1 μg/ml) and ATP (5.0 mM) induced RAW264.7 cells. (E) The effect of HSF1 overexpression on the ubiquitination of NLRP3 in LPS3h (1 μg/ml) and ATP (5.0 mM) induced RAW264.7 cells. (F) The effect of HSF1 knockout on the ubiquitination of NLRP3 in LPS3h (100 ng/ml) and ATP (2.5 mM) induced primary peritoneal macrophages. Data are representative or means (SD) of at least three independent experiments.