Figure 1: Laboratory workflow utilizing the saliva-based RT-qPCR diagnostic system.
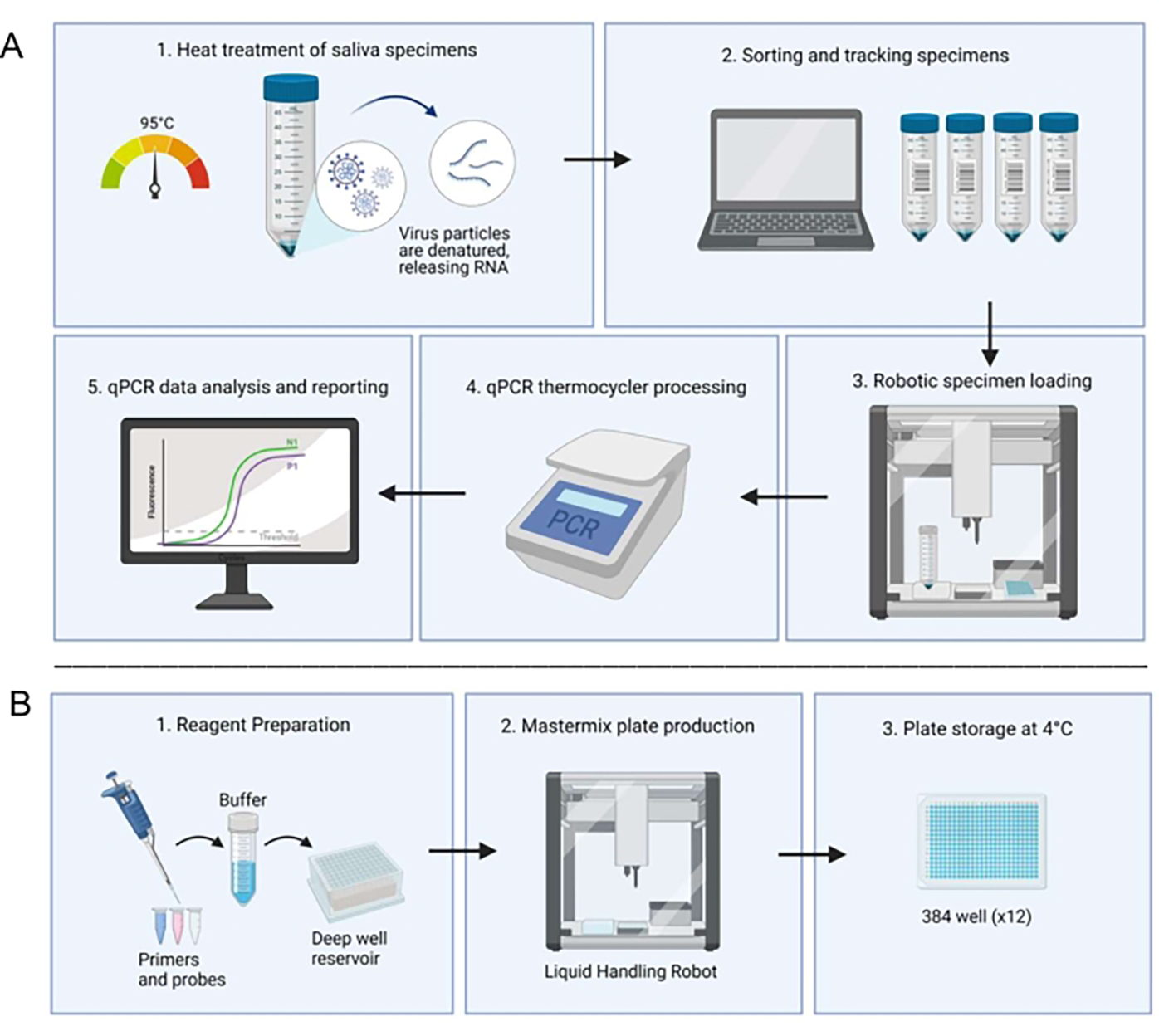
(A) Samples are collected and heat-treated at 95 °C for 30 min. Treated samples are sorted and tracked with patient information through an in-house spreadsheet system. A liquid handling robot loads samples into duplicate wells of prepared master mix plates. A technician manually loads the controls, seals the plate, and places the plate in a thermocycler for processing. Results are analyzed through an automated computer system and verified by a technician. (B) A technician prepares reagents for the master mix which are added to a deep well reservoir in a sterile biosafety cabinet. Filled deep well reservoirs are loaded into a dedicated liquid handling robot. Completed plates are sealed with foil, labeled, and stored at 4 °C.
