Figure 5: Comparison between manual and automated saliva transfer SARS-CoV-2 (N1) Ct values.
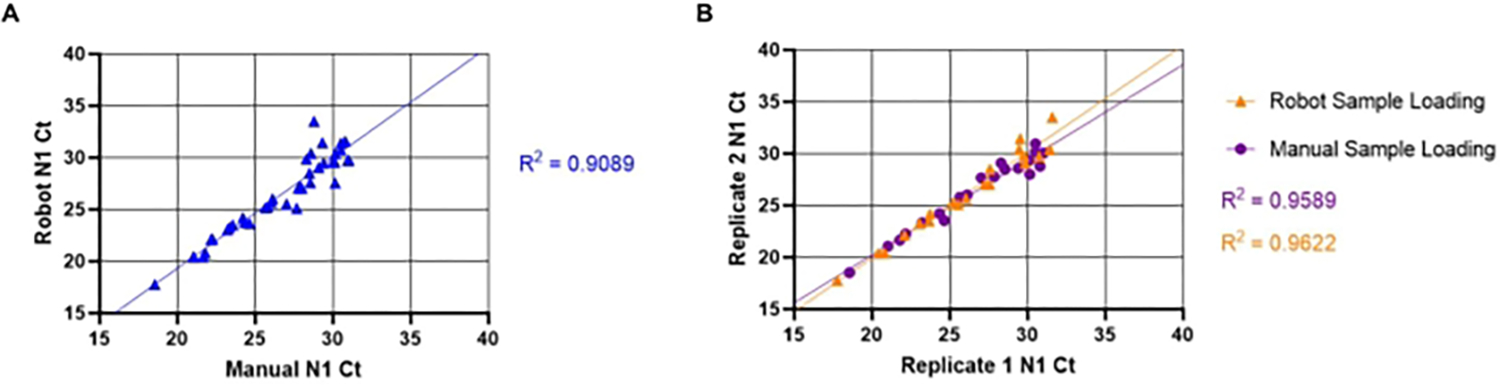
The known SARS-CoV-2 positive saliva samples (n =20) were loaded in duplicate into an RT-qPCR master mix plate by a liquid handling robot. The samples have a Ct value ranging from 18–32 for N1. The same samples were then manually loaded into duplicate wells in a different plate location. (A) N1 Ct values obtained from unique samples using both the robot and manual sample loading were transposed to determine inter-assay variability between manual and robot loading. (B) Intra-assay variability was also determined by using transposed replicate of N1 Ct values obtained from both robot and manual sample loading.
