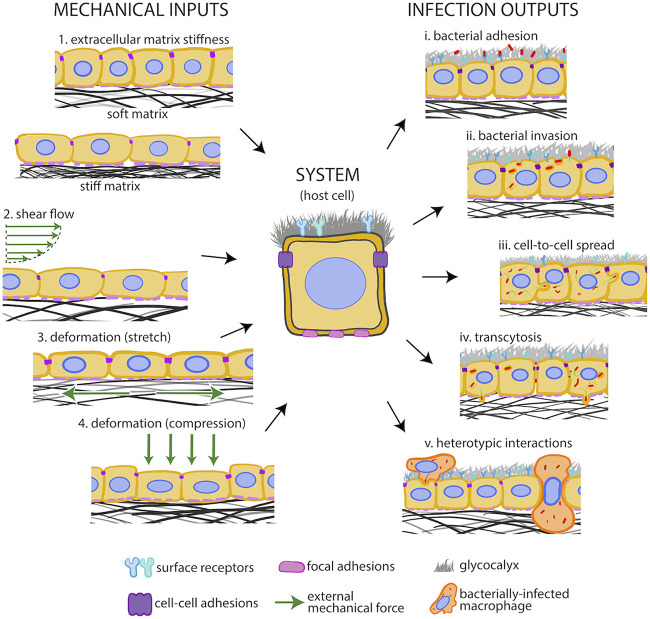
FIG 6.
Host cells experience extracellular mechanical cues during infection. Extracellular mechanical cues (input, left) imposed on host cells (system, middle) by their environment and the different host cell-pathogen interaction processes they could modulate (output, right). Extracellular mechanical cues include (1) ECM stiffness, (2) luminal shear flows, (3) cellular deformation due to ECM stretch, and (4) pressure-driven cellular compression. Host-pathogen interactions that could be modulated by extracellular mechanics include (i) adhesion of bacteria onto the host cell surface, (ii) uptake of bacteria within host cells (internalization), (iii) intracellular bacteria cell-to-cell spread, (iv) bacterial transmigration from the epithelial layer across the basement membrane, and (v) heterotypic bacterial spread from infected immune cells and infected immune cell transmigration through epithelia or endothelia.