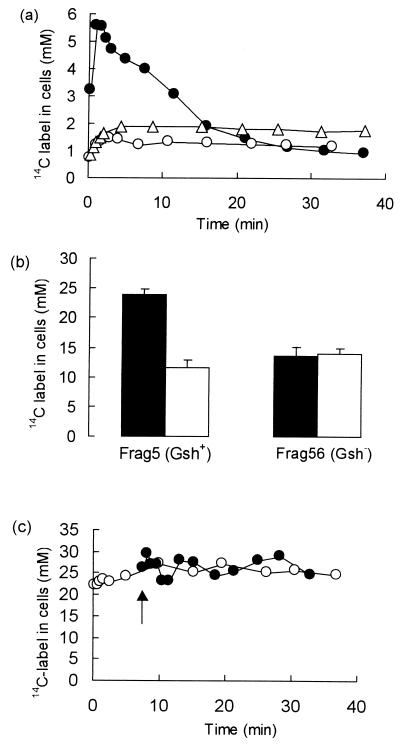
FIG. 1.
Metabolism of NEM by E. coli cells. Cells were grown to exponential phase in K120 medium and prepared for the determination of 14C-NEM metabolism as described in Materials and Methods. (a) Rapid metabolism of NEM takes place in E. coli cells. 14C-NEM (specific activity, 6.5 Ci · mol−1) was added to cells suspended in K0 (OD650 = 1), and samples were taken at intervals, filtered, and washed dropwise with 1 ml of prewarmed K0 medium. The filters were then dried, and the radioactivity was measured by scintillation counting. A standard aliquot of 14C-NEM was dried onto a filter for the estimation of counting efficiency. Symbols: ●, Frag5 (11 μM NEM); ○, Frag56 (GshA−) (12 μM NEM); ▵, Frag5 preincubated with 2 mM iodoacetate for 5 min with 16 μM NEM added. (b) Incubation with high concentrations of NEM forms a pool of osmotically active metabolites. Cells of Frag5 (GshA+) and Frag56 (GshA−) were grown in double-strength K120 medium to facilitate osmotic downshock and then incubated with 500 μM 14C-NEM (64 μC · μmol−1, final specific activity) for up to 30 min. At intervals the samples were filtered and washed with prewarmed medium, and then either the radioactivity was determined or the cells were subjected to osmotic downshock with ice-cold water (23) prior to determination of the radioactivity in the cells. Filled bars, without osmotic downshock; open bars, after osmotic downshock. (c) Rapid turnover of the ESG pool in cells incubated with high concentrations of NEM. Cells were grown in K120, washed, and suspended in K0 medium (OD650 = 0.9). Symbols: ○, 500 μM 14C-NEM (130 mCi · mol−1) added (t = 0); ●, 500 μM nonradioactive NEM added (t = 0) and 20 μM 14C-NEM added after 7 min (arrow) to a final specific activity of 204 mCi · mol−1. Samples were filtered, washed, and dried, and the radioactivity was determined.